The module <SSL> of the subsystem "Transports"
| Module: | SSL |
| Name: | SSL |
| Type: | Òðàíñïîðò |
| Source: | tr_SSL.so |
| Version: | 1.5 |
| Author: | Roman Savochenko, Maxim Lysenko (2009) |
| Description: | Provides transport based on the secure sockets' layer. OpenSSL is used and SSLv3 and TLSv1 are supported. |
| License: | GPL |
Introduction
The module SSL of the transport provides the support of transport based on secure sockets layer (SSL) into the system. In the basis of the module there is the library ![]() OpenSSL. Incoming and outgoing transports of protocols SSLv3 and TLSv1 are supported.
OpenSSL. Incoming and outgoing transports of protocols SSLv3 and TLSv1 are supported.
It is possible to add new incoming and outgoing transports through the transport subsystem configuration in any configurator of OpenSCADA system.
1. Incoming transports
The configured and running incoming transport opens server SSL-socket for the expectation of connection of the clients. SSL-socket is a multi-stream, ie when the client connects, the client SSL-connection and a new stream in which the client is served are created. Server SSL-socket in this moment switches to the waiting for the request from the new client. Thus the parallel service of the clients is achieved.
Each incoming transport is necessarily associated with one of the available transport protocols, to which incoming messages are transmitted. In conjunction with the transport protocol is supported by a mechanism of the combining of pieces of requests, disparate while transferring.
Configuration dialog of the incoming SSL-transport is depicted in Figure 1.
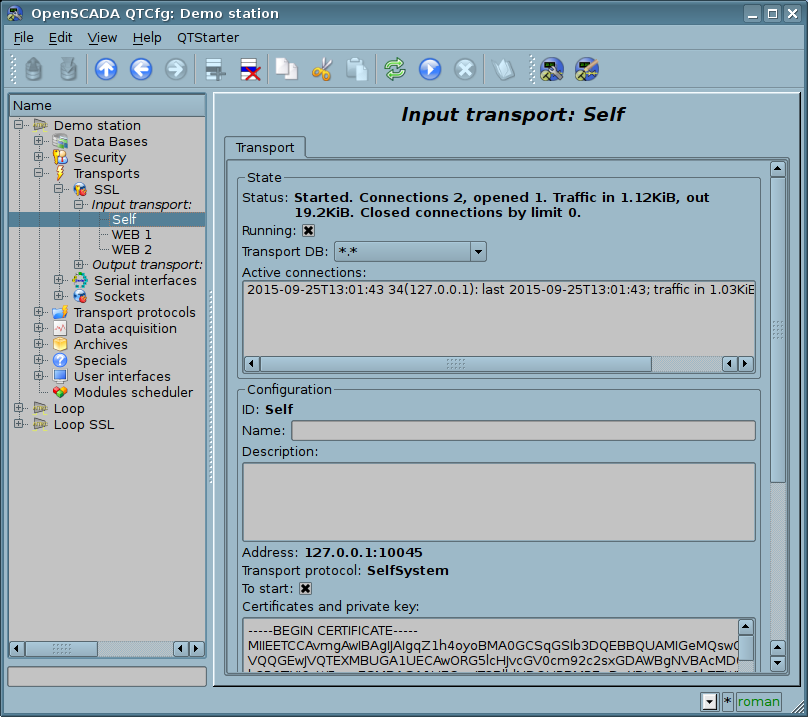
Fig.1. Configuration dialog of the incoming SSL-transport.
Using this dialog you can set:
- State of transport, namely: "Status", "Running", name of the database (containing the configuration) and list with information about the active connections.
- Id, name and description of transport.
- Address of the transport in the format: "[address]:[port]:[mode]", where:
- address – Address, on which the SSL is opened. It must be one of the addresses of the host. If the "*" is indicated then SSL will be available in all the host's interfaces. There may be as the symbolic representation as well as IP one of the address.
- port – Network port, on which the SSL is opened. Indication of the character name of the port (according to /etc/services) is available.
- mode – SSL-mode and version (SSLv3, SSLv23, TLSv1). By default and in case of error the SSLv23 is used.
- Choice of a transport protocol.
- State, in which the transport must be translated at boot: «To start».
- Certificates, private SSL key and password of private SSL key.
- Maximum number of clients to serve, maximum number of clients to serve per host and size of the input buffer.
- Keep alive requests. Close the connection after specified requests. Zero value for disable (not close ever).
- Keep alive timeout (s). Close the connection after no requests at specified timeout. Zero value for disable (not close ever).
- Transport's tasks priority.
2. Outgoing transports
Configured and running outgoing transport opens the SSL connection to the specified server. In the case of destroying of the connection, outgoing transport is disconnected. In order to resume the connection transport must be re-run.
Main tab of the configuration page of outgoing SSL-transport is shown in Fig.2.
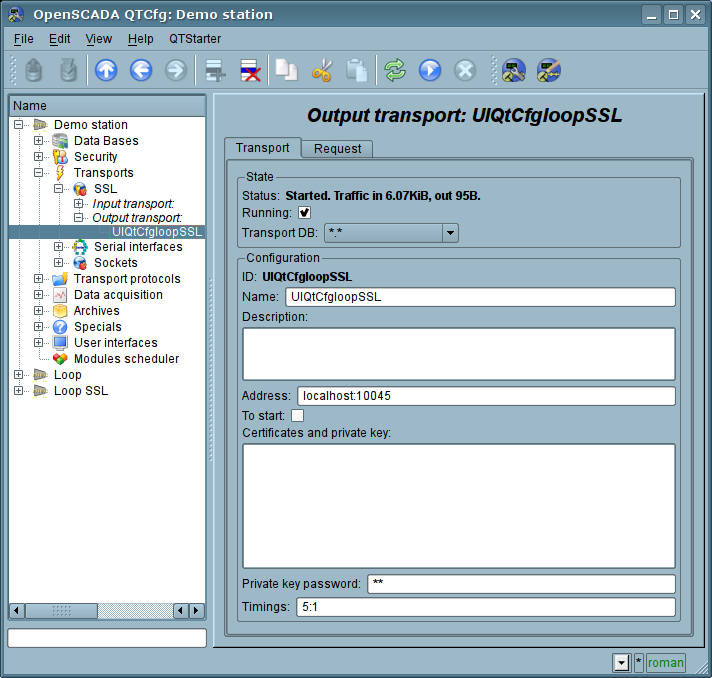
Fig.2. Main tab of the configuration page of the outgoing SSL-transport.
Using this dialog you can set:
- The state of transport, namely: "Status", "Running" and the name of the database, containing the configuration.
- Id, name and description of transport.
- Address of the transport in the format: "[address]:[port]:[mode]", where:
- address – Address with which the connection is made. There may be as the symbolic representation as well as IP one of the address.
- port – Network port with which the connection is made. Indication of the character name of the port (according to /etc/services) is available.
- mode – SSL-mode and version (SSLv3, SSLv23, TLSv1). By default and in case of error the SSLv23 is used.
- The state, in which the transport must be translated at boot: «To start».
- Certificates, private SSL key and password of private SSL key.
- Default timeout for connection and respond wait, separated.
3. Certificates and keys
For a valid module work certificates and private keys are required. In the case of the incoming SSL-transport (the server) they are compulsory. In the case of outgoing SSL-transport they can not be even installed though their using is desirable.
The simplest configuration of the certificate is self-subscription certificate and private key. The following describes how to create them using the tool openssl:
# Generation the secret key
$ openssl genrsa -out ./key.pem -des3 -rand /var/log/messages 2048
# Generation of self-subscription certificate
$ openssl req -x509 -new -key ./key.pem -out ./selfcert.pem -days 365
Next, the contents of the files key.pem and selfcert.pem is copied into the text field of the certificate and key. Password of the private key is installed in the appropriate field.
Links