Functional characteristics and demands of OpenSCADA system
The page contains information allowing to receive general representation about functions which the OpenSCADA system can carry out by the current moment. Functions are grouped on spheres of application of OpenSCADA system. For reception of a picture as a whole of functions planned or make now are included also. The page also have demands of OpenSCADA system for it building and execution.
1. The employment area of system OpenSCADA
Separating to the employment areas is made to simplify perception of the system functionality in light of traditional area for the project OpenSCADA — automation of technological processes. But also there possible mixed and specialized configuring systems for real-time data operation, for example into areas: ERP, Billing, Smart House and etc.
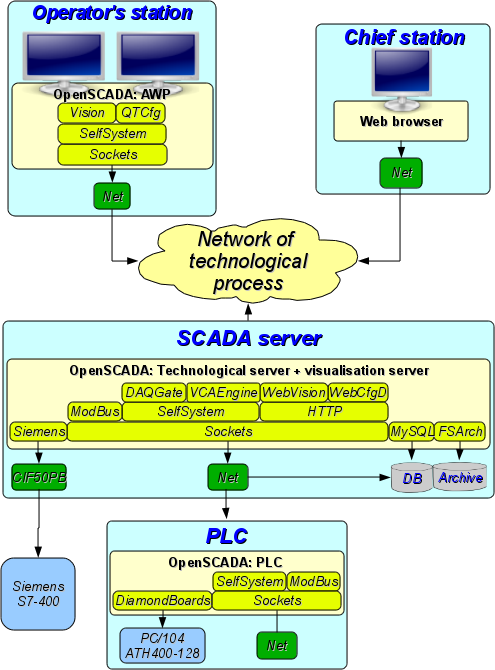
Fig. 1. OpenSCADA system's roles
1.1. SCADA system's server
- The visual control and management by means of the interfaces:
- Remote visualization server grounded on visualization and control area (VCA) engine VCAEngine. The module UI.Vision local starting and connecting to the visualization server.
- Remote WEB interface. By means of a Web-browser, the visualization module WebVision and the module of a kernel of visual control area VCAEngine.
- Simple remote Web-interfaces of user. By mean Web-browser and UI-module WebUser.
- Data acquisition (DAQ) from sources:
- Information about a platform (hardware-software) on which the server works. By means of the DAQ-module System.
- Data acquisition from sources which support protocol SNMP (Simple Network Management Protoñol). By means of the DAQ-module SNMP.
- Data acquisition from controllers of firm Siemens of S7 series. By means of the DAQ-module Siemens.
- Data acquisition of industrial controllers under the protocol ModBus. By means of the DAQ-module ModBus.
- Data acquisition of industrial controllers under the protocol DCON. By means of the DAQ-module DCON.
- Formation of derivative structures of parameters on the basis of templates of parameters and data from other sources. By means of the DAQ-module LogicLev.
- Data acquisition from other servers and PLC, based on OpenSCADA, possibly for duplication. By means of the DAQ-module DAQGate.
- Data acquisition from sound controller's input channels. By means of the DAQ-module SoundCard.
- Data acquisition from hardware of firm
 ICP DAS. By means of the DAQ-module ICP_DAS.
ICP DAS. By means of the DAQ-module ICP_DAS.
- Data acquisition from sources which support protocol OPC-UA. By means of the DAQ-module OPC-UA.
- Data acquisition from automation of "Big Dutchman" company. By means of the DAQ-module BFN.
- Data acquisition from sources DAQ-boars on buses ISA, PCI, PCMCIA and USB by means library of the project
 Comedi and the DAQ-module Comedi.
Comedi and the DAQ-module Comedi.
- Data acquisition from different sources, which have utilities for access to it data or it accessibly through simple special network protocols. Made by getting procedure writing on language of user programming by DAQ-module JavaLikeCalc, and also transport-protocol-module User Protocol. Most known protocols implementing on the Users Protocols: SMS, SMTP, Elemer TM510x, EDWARDS TURBOMOLECULAR PUMPS (SCU750), Heat counter computer VKT7, Sycon Multi Drop Protocol, Power supply for turbomolecular pumps (TMP-xx03), Temperature measurement IT-3, OWEN, IVE-452HS-02, OPTRIS CT/CTL, CTR 100-101, IEC-60870-104, I2C Chips (PCF8591, PCF8574, DS3231, AT24CXX), 1Wire Chips by adapters DS9097 and DS9097U (DS1820, DS1820/DS18S20/DS1920, DS1822, DS2413, DS2408, DS2450, DS2438), Low level devices by GPIO (DHT, 1602A), etc.
- Providing data to upper-level systems:
- By means of interfaces:
- By means of protocols:
- Self OpenSCADA protocol, by helps of transport's protocol module SelfSystem.
- ModBUS family protocol (TCP, RTU and ASCII), by helps of transport's protocol module ModBUS.
- "OPC-UA" protocol, by helps of transport's protocol module OPC-UA.
- Simple special protocols, developed by users by helps of transport's protocol module User Protocol.
- Implementation of user calculations in languages:
- Language of block schemes. By means of the DAQ-module BlockCalc.
- With the help of Java-like language of a high level. By means of the DAQ-module JavaLikeCalc.
- Archiving messages, conducting reports on various categories and levels by means of mechanisms:
- Archiving values of the collected data by means of mechanisms:
- Configuration and management of a server through:
- The WEB-interface. By means of a Web-browser and the UI-module WebCfgD and WebCfg.
- From the remote configuration station. By means of the UI-module at configuration station QTCfg and the interface of management OpenSCADA reflected in the protocol SelfSystem.
- Data storage of a server in a DB of types:
- MySQL. By means of the DB-module MySQL.
- SQLite. By means of the DB-module SQLite.
- PostgreSQL. By means of the DB-module PostgreSQL.
- DBF. By means of the DB-module DBF.
- FireBird. By means of the DB-module FireBird.
- In plans. DB accessible on other server based on OpenSCADA.
- In plans. LDAP.
1.2. Station of the operator of technological process, the board of the dispatcher, the panel of monitoring, etc.
- The visual control and management by means of the interfaces:
- The local (fast) interface based on QT library. By means of the visualization module Vision and the module of a kernel of the visual control area VCAEngine include ability of visualization from remote engine of VCA, visualization server.
- Remote WEB interface. By means of a Web-browser, the visualization module WebVision and the module of a kernel of visual control area VCAEngine.
- Simple remote Web-interfaces of user. By mean Web-browser and UI-module WebUser.
- Data acquisition (DAQ) from sources:
- Data acquisition from other servers and PLC, based on OpenSCADA, for data transportation and for duplication. By means of the DAQ-module DAQGate.
- Data acquisition from sources which support protocol SNMP (Simple Network Management Protoñol). By means of the DAQ-module SNMP.
- Data acquisition from sources which support protocol OPC-UA. By means of the DAQ-module OPC-UA.
- Implementation of the user calculations in languages:
- Language of block schemes. By means of the DAQ-module BlockCalc.
- With the help of Java-like language of a high level. By means of the DAQ-module JavaLikeCalc.
- Archiving messages, conducting reports on various categories and levels by means of mechanisms:
- Configuration and management of station through:
- The WEB-interface. By means of a Web-browser and the UI-module WebCfgD or WebCfg.
- The QT-interface. By means of the UI-module QTCfg.
- From the remote configuration station. By means of the UI-module at configuration station QTCfg and the interface of management OpenSCADA reflected in the protocol SelfSystem.
- Data storage of station in a DB of types:
- MySQL. By means of the DB-module MySQL.
- SQLite. By means of the DB-module SQLite.
- PostgreSQL. By means of the DB-module PostgreSQL.
- DBF. By means of the DB-module DBF.
- FireBird. By means of the DB-module FireBird.
- In plans. DB accessible on other server based on OpenSCADA.
- In plans. LDAP.
1.3. The environment of execution of controllers (PLC)
- Data acquisition (DAQ) from sources:
- Cards of data acquisition of firm
 Diamond Systems. By means of the DAQ-module DiamondBoards.
Diamond Systems. By means of the DAQ-module DiamondBoards.
- Information on a platform (hardware-software) on which the server works. By means of the DAQ-module System.
- Data acquisition from sources which support protocol SNMP (Simple Network Management Protoñol). By means of the DAQ-module SNMP.
- Data acquisition of industrial controllers under the protocol ModBus. By means of the DAQ-module ModBus.
- Data acquisition of industrial controllers under the protocol DCON. By means of the DAQ-module DCON.
- Formation of derivative structures of parameters on the basis of templates of parameters and data from other sources. By means of the DAQ-module LogicLev.
- Data acquisition from other servers and PLC, based on OpenSCADA, possibly for duplication. By means of the DAQ-module DAQGate.
- Data acquisition from sound controller's input channels. By means of the DAQ-module SoundCard.
- Data acquisition from hardware of firm
 ICP DAS. By means of the DAQ-module ICP_DAS.
ICP DAS. By means of the DAQ-module ICP_DAS.
- Data acquisition from sources which support protocol OPC-UA. By means of the DAQ-module OPC-UA.
- Data acquisition from sources DAQ-boars on buses ISA, PCI, PCMCIA and USB by means library of the project
 Comedi and the DAQ-module Comedi.
Comedi and the DAQ-module Comedi.
- Data acquisition from different sources, which have utilities for access to it data or it accessibly through simple special network protocols. Made by getting procedure writing on language of user programming by DAQ-module JavaLikeCalc, and also transport-protocol-module User Protocol. Most known protocols implementing on the Users Protocols: SMS, SMTP, Elemer TM510x, EDWARDS TURBOMOLECULAR PUMPS (SCU750), Heat counter computer VKT7, Sycon Multi Drop Protocol, Power supply for turbomolecular pumps (TMP-xx03), Temperature measurement IT-3, OWEN, IVE-452HS-02, OPTRIS CT/CTL, CTR 100-101, IEC-60870-104, I2C Chips (PCF8591, PCF8574, DS3231, AT24CXX), 1Wire Chips by adapters DS9097 and DS9097U (DS1820, DS1820/DS18S20/DS1920, DS1822, DS2413, DS2408, DS2450, DS2438), Low level devices by GPIO (DHT, 1602A), etc.
- Cards of data acquisition of firm
- Providing data to upper-level systems:
- By means of interfaces:
- By means of protocols:
- Self OpenSCADA protocol, by helps of transport's protocol module SelfSystem.
- ModBUS family protocol (TCP, RTU and ASCII), by helps of transport's protocol module ModBUS.
- "OPC-UA" protocol, by helps of transport's protocol module OPC-UA.
- Simple special protocols, developed by users by helps of transport's protocol module User Protocol.
- Management, regulation and performance of other user calculations in languages:
- Language of block schemes. By means of the DAQ-module BlockCalc.
- With the help of Java-like language of a high level. By means of the DAQ-module JavaLikeCalc.
- Archiving messages, conducting reports on various categories and levels by means of mechanisms:
- Archiving of values of the collected data by means of mechanisms:
- Configuration and management PLC through:
- The WEB-interface. By means of a Web-browser and the UI-module WebCfgD or WebCfg.
- From the remote configuration station. By means of the UI-module at configuration station QTCfg and the interface of management OpenSCADA reflected in the protocol SelfSystem.
- Data storage PLC in a DB of types:
- All data in a configuration file (fixed).
- MySQL. By means of the DB-module MySQL.
- SQLite. By means of the DB-module SQLite.
- PostgreSQL. By means of the DB-module PostgreSQL.
- DBF. By means of the DB-module DBF.
- FireBird. By means of the DB-module FireBird.
- In plans. DB accessible on other server based on OpenSCADA.
- In plans. LDAP.
1.4. Universal OPC-UA server
Due implementation of the protocol OPC-UA into agent mode, OpenSCADA can provide popular function of the OPC-server to client's protocols, which supports and direct implemented into OpenSCADA. The function common uses on platform MS Windows®, and many SCADA-systems on the platform work exclusively with OPC—servers, as the data sources. Thus OpenSCADA can act by universal OPC-server on Linux platform (Fig.2).
In plans. With adapting OpenSCADA for work on MS Windows® platform and implementing work with OPC-DA by system DCOM, there will appear possibility for applying OpenSCADA into gate OPC-DA -> OPC-UA role, which means free integration of old systems to the new or accumulation systems.
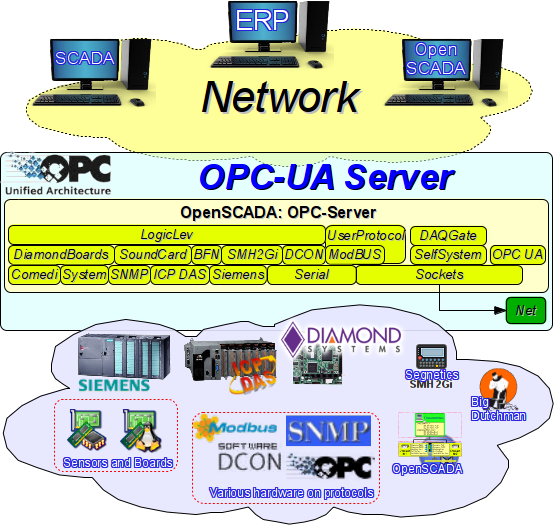
Fig. 2. OpenSCADA system role as "OPC-UA Server".
The data sources and protocols, which accessible by the unified OPC-UA server:
- The industrial controllers of firm
 Siemens GMBH series S7, DAQ.Siemens.
Siemens GMBH series S7, DAQ.Siemens.
- The hardware firm
 ICP DAS, DAQ.ICP_DAS.
ICP DAS, DAQ.ICP_DAS.
- The data acquisition boards firm
 Diamond Systems, DAQ.DiamondBoards.
Diamond Systems, DAQ.DiamondBoards.
- The wide range of DAQ-boards Devices Object Interface (DOI) of different producers at buses ISA, PCI, PCMCIA and USB by library of project
 Comedi, DAQ.Comedi.
Comedi, DAQ.Comedi.
- The wide range of industrial controllers and other data sources by protocol ModBus, DAQ.ModBus.
- The wide range of industrial controllers and other data sources by protocol DCON, DAQ.DCON.
- The wide range of data of network hardware by protocol "Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP)", DAQ.SNMP.
- The data sources which supports protocol OPC_UA (gating "OPC-UA") or wide range of data sources accessible for all sort OPC, by proper gate to OPC-UA, DAQ.OPC_UA.
- The wide range of industrial controllers and other data sources by protocol MMS(IEC-9506), DAQ.MMS.
- The data of other servers and PLC based at OpenSCADA, DAQ.DAQGate.
- Working into the PLC SMH 2Gi of firm
 Segnetics, with it DOI, DAQ.SMH2Gi.
Segnetics, with it DOI, DAQ.SMH2Gi.
- Automatic of poultry farming by
 Big Dutchman, DAQ.BFN.
Big Dutchman, DAQ.BFN.
- The data of commercial counting and simple resources counting with the complex enough interaction protocol, DAQ.AMRDevs (RU).
- The sensors of platform (software-hardware) on that the server running, DAQ.System.
- The data of inputs of sound controllers of PC, DAQ.SoundCard.
- The calculated, internal or intermediate data by high level internal programming language (DAQ.JavaLikeCalc) and language of blocks schemes (DAQ.BlockCalc).
- Derivative structures of parameters-objects based at the parameter's templates and other sources data, DAQ.LogicLev.
- The data sources of different types, which have console utilities for the data access or accessible by simple specialized network protocols. Performed by writing some procedure of getting the data at the language of user-level programming (DAQ.JavaLikeCalc), and also the module of transport protocols (Protocol.UserProtocol), see the library.
2. Requirements for OpenSCADA
2.1. Execution
The demands to apparatus for OpenSCADA system execution at different roles viewed into table 1. The demands to programs for OpenSCADA system execution and it modules allow into table 2.
Table 1. The demands to apparatus for OpenSCADA system and it modules.
| Role | Demands |
| SCADA system's server | CPU: x86_32 (more than i586), x86_64 or ARM, with frequency more 500 MHz MEM: 128 MB HDD: 10 GB include OS and place for archives |
| Station of the operator of technological process, the board of the dispatcher, the panel of monitoring, etc. | CPU: x86_32 (more than i586), x86_64 or ARM, with frequency more 1 GHz MEM: 512 MB HDD: 4 GB include OS without archives place |
| The environment of execution of controllers (PLC) | CPU: x86_32 (more than i586), x86_64 or ARM, with frequency more 133 MHz MEM: 32 MB HDD: 32 MB include OS without archives place. |
Table 2. Dependences of performance of OpenSCADA system and its modules.
| Component | Description |
| Dependences of OpenSCADA system's kernel | |
| OS Linux | The distribution kit of operating system Linux (ALTLinux, SuSELinux, Mandriva, ASPLinux, Fedora, Debian, Ubuntu ...) |
| "Standard libraries" | Standard set of libraries: GLibC (>= 2.3) or uCLibC (>= 0.9.32) and libstdc++ (>= 3.3). Certainly this already allow into installed distribution. Special demand is using native thread library NPTL, already used for all modern distributions of the Linux. |
| zlib | Compression library. |
| libpcre | Library for use regular expressions, compatible with Perl. |
| libgd (opt: --enable-LibGD) | Graphic library GD version 2, it is desirable that it will be without XPM support (dependence on library of a X-server is excluded) and support of FontConfig. |
| DB.MySQL module | |
| libMySQL | Library for access to MySQL DBMS. |
| DB.SQLite module | |
| libsqlite3 | Library for access to built in DB SQLite version 3. |
| DB.PostgreSQL module | |
| libpq | Library for access to PostgreSQL DBMS version more 8.3.0. |
| DB.FireBird module | |
| FirebirdSS | FireBird DBMS version 2. Often is absent in distribution kits of Linux and demands individual loading from an official site ( |
| Transport.SSL module | |
| libssl | Library for codifying OpenSSL. |
| DAQ.SNMP module | |
| libsnmp | Library for access to data of network devices under SNMP protocol. |
| DAQ.System module | |
| libsensors (opt: auto) | Hardware sensors' library versions 2 and 3. |
| DAQ.SoundCard module | |
| libportaudio | Multiplatform library for access to sound controller version 19 and higher (not 18). |
| DAQ.OPC_UA module | |
| libssl | Library for codifying OpenSSL. |
| DAQ.Comedi module | |
| libcomedi | Library of realizing support for DAQ-boards different manufacturer on boards ISA, PCI, PCMCIA and USB. |
| Modules: UI.QTStarter, UI.QTCfg | |
| libQT4 (libQtGui) or libQt5 (libQt5Widgets,libQt5PrintSupport) | Library for construction of user graphic interface QT version 4.3 and higher or 5.1 and higher. |
| Module: UI.Vision | |
| libQT4 (libQtGui) or libQt5 (libQt5Widgets,libQt5PrintSupport) | Library for construction of user graphic interface QT version 4.3 and higher or 5.1 and higher. |
| libQtWebKit (opt: auto) | Library of Web-rendering engine WebKit. |
| libfftw3 (opt: auto) | Library for fast Fourie transfer of signals. |
| libphonon (opt: auto) | Library for full formatted video and audio play. |
| Modules: UI.WebVision, Special.FLibSYS | |
| libfftw3 (opt: auto) | Library for fast Fourie transfer of signals. |
2.2. Building
Dependencies of system OpenSCADA for building of the OpenSCADA kernel and its modules are tabulated bellow.
Table 3. Dependencies of building of OpenSCADA system and its modules.
| Component | Description |
| The general requirements for building OpenSCADA | |
| OS Linux | The distribution kit of operating system Linux (ALTLinux, SuSELinux, Mandriva, ASPLinux, Fedora, Debian, Ubuntu ...) |
| g++ | The compiler of language C++ version 3.3 and more from a collection of compilers GCC, including library GLibC (>=2.3) or uCLibC (>= 0.9.32). |
| autotools (autoconf, automake, libtool, pkg-config) | Tools for formation of building environment of OpenSCADA. They are necessary only in the case of changing building environment of OpenSCADA, for example for addition of the new module or change of the fixed parameters of building. Automake >= 1.9. |
| gettext | Group of utilities for preparation and compilations of translations of the interface of programs on various languages in conformity with internationalization standard I18N. |
| sqlite3 | Control utility for DB SQLite3 files. |
| zlib (devel) | Compression library, a package for development. |
| libpcre (devel) | Library for use regular expressions, compatible with Perl, a package for development. |
| libgd (devel, opt: --enable-LibGD) | Graphic library GD version 2, a package for development, it is desirable that it will be without XPM support (dependence on library of a X-server is excluded) and support of FontConfig. It is used for construction of trends and other images in PNG format. |
| DB.MySQL module | |
| libMySQL (devel) | Library for access to MySQL DBMS, a package for development on language C. |
| DB.SQLite module | |
| libsqlite3 (devel) | Library for access to built in DB SQLite version 3, a package for development. |
| DB.PostgreSQL module | |
| libpq | Library for access to PostgreSQL DBMS version more 8.3.0, a package for development. |
| DB.FireBird module | |
| FirebirdSS | FireBird DBMS version 2, a package for development. Often is absent in distribution kits of Linux and demands individual loading from an official site ( |
| Transport.SSL module | |
| libssl (devel) | Library for codifying OpenSSL, a package for development. |
| DAQ.JavaLikeCalc module | |
| bison | The program of generation of parsers on the basis of grammar of language. |
| DAQ.SNMP module | |
| libsnmp (devel) | Library for access to data of network devices under SNMP protocol, a package for development. |
| DAQ.System module | |
| libsensors (devel, opt: auto) | Hardware sensors' library versions 2 and 3, a package for development. |
| DAQ.Siemens module | |
| glibc-kernheaders | Linux-kernel headers by library GLibC. |
| DAQ.SoundCard module | |
| libportaudio (devel) | Multiplatform library for access to sound controller, a package for development version 19 and higher (not 18). |
| DAQ.OPC_UA module | |
| libssl (devel) | Library for codifying OpenSSL, a package for development. |
| DAQ.Comedi module | |
| libcomedi (devel) | Library of realizing support for DAQ-boards different manufacturer on boards ISA, PCI, PCMCIA and USB, package for development. |
| Modules: UI.QTStarter, UI.QTCfg | |
| libQT4 or libQT5 (devel) | Library for construction of user graphic interface QT version 4.3 and higher or 5.1 and higher, package for development. |
| Module: UI.Vision | |
| libQT4 or libQT5 (devel) | Library for construction of user graphic interface QT version 4.3 and higher or 5.1 and higher, package for development. |
| libQtWebKit (devel, opt: auto) | Library of Web-rendering engine WebKit, package for development. |
| libfftw3 (devel, opt: auto) | Library for fast Fourie transfer of signals, package for development. |
| libphonon (devel, opt: auto) | Library for full formatted video and audio play, package for development. |
| Modules: UI.WebVision, Special.FLibSYS | |
| libfftw3 (devel, opt: auto) | Library for fast Fourie transfer of signals, package for development. |
3. Links