The modules <ModBus> of subsystems "Data acquisition" and "Transport protocols"
| Parameter | Module 1 | Module 2 |
| ID: | ModBus | |
| Name: | ModBus | |
| Type: | DAQ | Protocol |
| Source: | daq_ModBus.so | |
| Version: | 1.8.0 | 1.0.0 |
| Author: | Roman Savochenko | |
| Translated: | Maxim Lysenko | |
| Description: | Provides implementation of client service of the protocol ModBus. ModBus/TCP, ModBus/RTU and ModBus/ASCII protocols are supported. | Provides implementation of protocols ModBus. ModBus/TCP, ModBus/RTU and ModBus/ASCII protocols are supported. |
| License: | GPL | |
Introduction
ModBus — communication protocol based on the client-server architecture. It was developed by Modicon for using in the programmable logic controllers (PLC). It became the de facto standard in the industry and is widely used for the connection of industrial electronic equipment. Used to transfer data via serial line RS-485, RS-422, RS-232, and network TCP/IP. Currently supported non-profit organization ModBus-IDA.
There are three modes of the protocol: ModBus/RTU, ModBus/ASCII and ModBus/TCP. The first two use the serial communication lines (mostly RS-485, less RS-422/RS-232), the last uses TCP/IP network to transfer data.
The module of the data acquisition provides an opportunity to gather the information from various devices by means of the protocol ModBus in all modes. Also, the module implements the functions of the horizontal reservation, namely, working in conjunction with the remote station of the same level. At the same time, the module of the protocol allows you to create and issue data by means of the protocol ModBus in various modes, and through interfaces that are supported by modules of subsystem "Transports".
1. General description of the ModBus protocol
Protocol ModBus/RTU requires one lead(requesting) device in the line(master), which can send commands to one or more driven devices(slave), referring to them by a unique in the line address. Syntax of the commands of the protocol allows to address 247 devices on the one connection line of standard RS-485(less RS-422 or RS-232). In the case of TCP addressing mode is excluded from the protocol, as it is implemented in the TCP/IP stack.
Initiative of exchange always comes from the leading device. Slave devices listen the line. Master request (package, the sequence of bytes) in the line and turns into a listening line. Slave device responds to the request, which came to him.
The end of sending the response is determined by the mode. In RTU mode, the end of massage is determined by time interval between end of receive the previous byte and start receiving following, the time symbol. If this interval exceeds the time required to receiving one and a half bytes on a given rate of transmission then receiving a frame response is considered complete. In ASCII mode, the criterion of end of the massage is the character '\r', and in the mode of TCP — the expected size of the massage, information about which present in the packet header.
1.1. Addressing
All data operations are tied to zero, each type of data (register, bit, register of input or bit of input) addresses begin with 0 and ends 65535.
1.2. Standard codes of functions
In ModBus protocol it can be divided into several subsets of commands(Table 1).
Table 1: The subset of commands of ModBus protocol
| Subset | Range of codes |
| Standard | 1-21 |
| Reserve for advanced features | 22-64 |
| Custom | 65-119 |
| Reserve for own needs | 120-255 |
Data acquisition module uses commands 0x03 and 0x06(0x10) for read and write registers, 0x01 and 0x05(0x0F) for read and write bits, 0x02 and 0x04 for read bit and register of input accordingly. For other atypical commands implementation the module provides function of user programming API, which you can call from the template's procedure, sending arbitrary PDU packages and process received.
Protocol module process the requests by the commands 0x03 and 0x06(0x10) for reading and writing registers, 0x01 and 0x05(0x0F) for reading and writing bits.
2. Module of the implementation of the protocol
ModBus protocol module contains the code implementing of the protocol part of ModBus, namely particular variants of protocols ModBus/TCP, ModBus/RTU and ModBus/ASCII. Module of the protocol in conjunction with the selected transport is actively used by the data acquisition module for direct queries implementation. Because of the module of the protocol is independent, by using of it you can create additional modules for data acquisition by non-standard functions of the expansion of ModBus of various automation equipment.
2.1. API functions of outgoing requests
API functions for outgoing queries (messIO()) operate with the exchange of blocks PDU, XML-wrapped in packages with the following structure:
Where:
- prt — name of the tag with the name of the used variant of the protocol (TCP, RTU or ASCII).
- sId — identifier of the source of the query. Used for placing to the report of the output protocol.
- reqTm — time of the request, namely the time during which the answer is expected, in milliseconds.
- node — number of the destination node or the identifier of the unit ModBus/TCP.
- reqTry — number of attempts of repeating the request with the error in the answer. Only for ModBus/RTU and ModBus/ASCII.
- pdu — directly block of the unit of the protocol data (PDU) ModBus.
The resulting pdu replaces the request pdu in the XML-package, and set the attribute "err" to the code and text of the errors, if it is took place.
2.2. Servicing of the requests for ModBus protocol
Input part of servicing of the requests to the module of the protocol realizes verification and processing of the requests through objects of the nodes, provided by the module(Fig. 1). Actually, the mechanism is implemented, that allow the system OpenSCADA to perform the role of the ModBus/TCP server or the slave device of ModBus/RTU and ModBus/ASCII. Thus the system OpenSCADA gets an opportunity to serve the role of any participant of the ModBus networks.
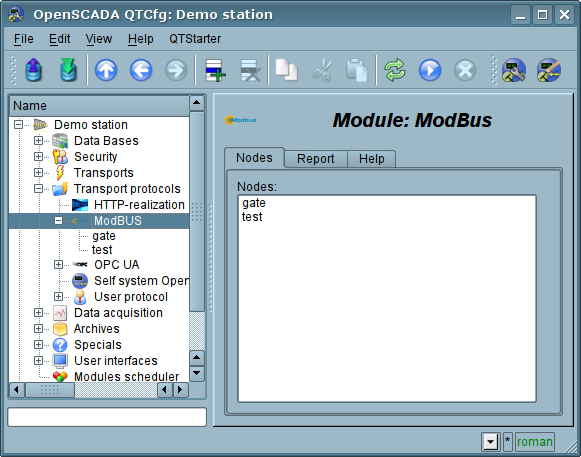
Fig.1. Tab of the list of the nodes of servicing incoming requests of the protocol.
The node of the protocol is equivalent to the physical node of the device of ModBus network. Node of the protocol can operate in three modes:
- "Data" — mode of the reflection of data of OpenSCADA on arrays of registers and bits of ModBus to transfer them at the request of the client node or master.
- "Gateway of the node" — mode of the redirecting of the requests to the node of the another ModBus network through this node.
- "Gateway of the network" — mode of the redirecting of the requests to any node in another ModBus network, actually carrying out the integration of several ModBus networks into one.
Since the protocol nodes can be created a great number, it turns out that on the one interface, ie in the one network, one station on the basis of OpenSCADA can clear provide multiple nodes of ModBus network with different data.
Lets consider particular configuration of the node of the protocol in various modes.
The mode of the node of the protocol "Data"
The mode is used to reflect the data of OpenSCADA on arrays of registers and bits of ModBus. The overall configuration of the node is made in the tab "Node"(Fig. 2) by the parameters:
- The state of the node, as follows: «Enable» and the name of the database containing the configuration.
- Id, name and description of the node.
- The state, in which the node must be translated at boot: «To enable».
- Address of the node in the ModBus network from 1 to 247.
- Inbound traffic, to the network of which the node is belonged to. It is selected from the list of input transport of the subsystem "Transports" of OpenSCADA. Specifying as the transport the symbol "*" makes this node a participant of any ModBus network with the processing of requests from any transport.
- Variant of the ModBus protocol, requests in which must be processed by the node from the list: All, RTU, ASCII, TCP/IP.
- The choice of the mode, in this case the mode "Data".
- Period of calculation of data in seconds. Specifies the frequency of processing of forming for the requests data, namely: data tables of ModBus, calculation of data programs and servicing of links to the data of OpenSCADA.
Node in this mode process the following standars commands of the ModBus protocol:
- 0x01 — reading of the group of bits;
- 0x02 — reading of the group of input bits;
- 0x03 — reading of the group of registers;
- 0x04 — reading of the group of input registers;
- 0x05 — settig of the single bit;
- 0x06 — settig of the single register;
- 0x0F — settig of the group of bits;
- 0x10 — settig of the group of registers.
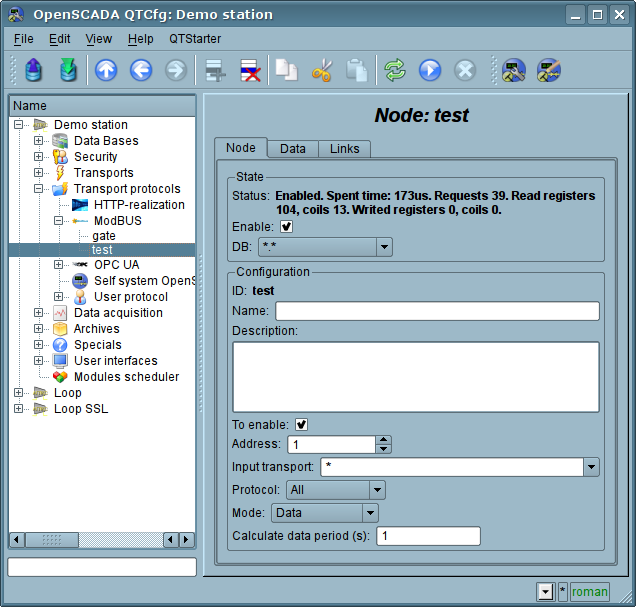
Fig.2. The tab "Node" of the configuration page of the node of the protocol in the "Data" mode.
To form the table of the reflection of the data of ModBus network, namely, registers and bits the tab "Data" is provided(Fig.3). The tab "Data" contains a table of parameters and program for processing of the parameters with the specified programming language, which is available in the system OpenSCADA. Table contains the parameters with the properties:
- Id — ID of the parameter. It is the key for the formation of the tables of registers and bits of ModBus. Registers and bits of ModBus set as follows:
R{N}[w], RI{N}[w] — specific register (and input) form, can expanded by suffixes: "i"—Int32, "f"—Float, "d"—Double, "s"—String (size by default is 10 and up to 100 registers);
R:{N}:[w], RI:{N}:[w] — classic register (and input) form, can expanded by suffixes: "i4"—Int32, "i8"—Int64, "f"—Float, "d"—Double, "s"—String
C{N}[w], CI{N}[w], C:{N}:[w], CI:{N}:[w] — coil (and input).
Where:
{N} — ModBus device's data address (decimal, hexadecimal or octal) [0...65535];
w — optional symbol for writing allow indicate.
Examples:
"R0x300w" — register access;
"C100w" — coin access, allow for write;
"R_f200" — get float from registers 200 and 201;
"R_i400,300" — get int32 from registers 400 and 300;
"R_s15,20" — get string, registers block, from register 15 and size 20.
"R_i8:0x10:w" — get and set int64 into registers [0x10-0x13];
"R_d:0x20,0x30" — get double float point (8 byte) from registers [0x20,0x30-0x32].
The table by default identifies several parameters of special appointment:
- f_frq — frequency of computing the table by the program;
- f_start — sign of the first computing — the start up of the program.
- f_stop — sign of the last execution — the stop of the program.
arguments["R_s10,5w"] = "9876543210";
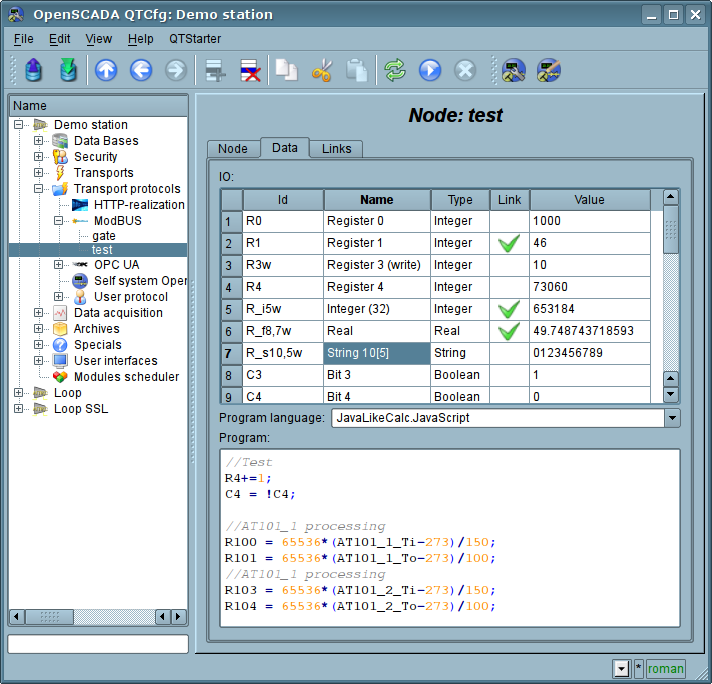
Fig.3. The tab "Data" of the configuration page of the node of the protocol in the "Data" mode.
For the parameter which are signed as links above it can be set the links only to switched off node of the protocol in the tab "Connections"(Figure 4).
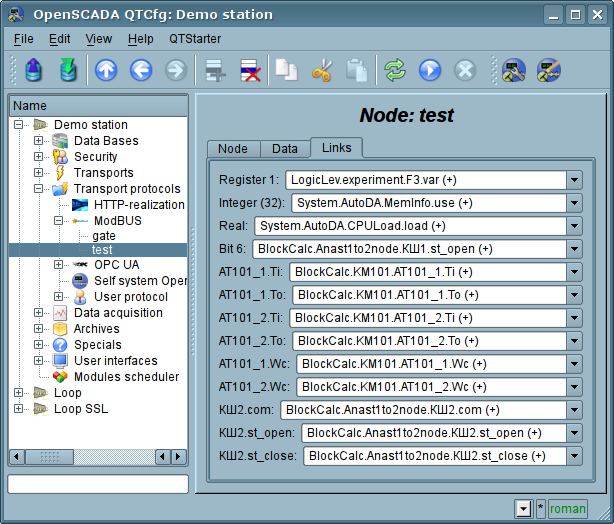
Fig.4. The tab "Links" of the configuration page of the node of the protocol in the "Data" mode.
The mode of the node of the protocol "Gateway of the node"
Mode is used to carryover the requests to a separate device in the other ModBus network from the ModBus network, in which this node is configured. The overall configuration of the node is made in the tab "Node"(Fig. 5) by the parameters:
- The state of the node, as follows: Status, «Enable» and the name of the database containing the configuration.
- Id, name and description of the node.
- The state, in which the node must be translated at boot: «To enable».
- Address of the node in the ModBus source network from 1 to 247.
- Inbound traffic, to the network of which the node is belonged to. It is selected from the list of input transport of the subsystem "Transports" of OpenSCADA. Specifying as the transport the symbol "*" makes this node a participant of any ModBus network with the processing of requests from any transport.
- Variant of the ModBus protocol, requests in which must be processed by the node from the list: All, RTU, ASCII, TCP/IP.
- The choice of the mode, in this case the mode "Gateway of the node".
- Transport, in which the request must be redirected, from the list of outgoing transports of subsystem "Transports".
- Protocol in which to redirect the request.
- Address of the node of ModBus network from 1 to 247, in which the request is forwarded to.
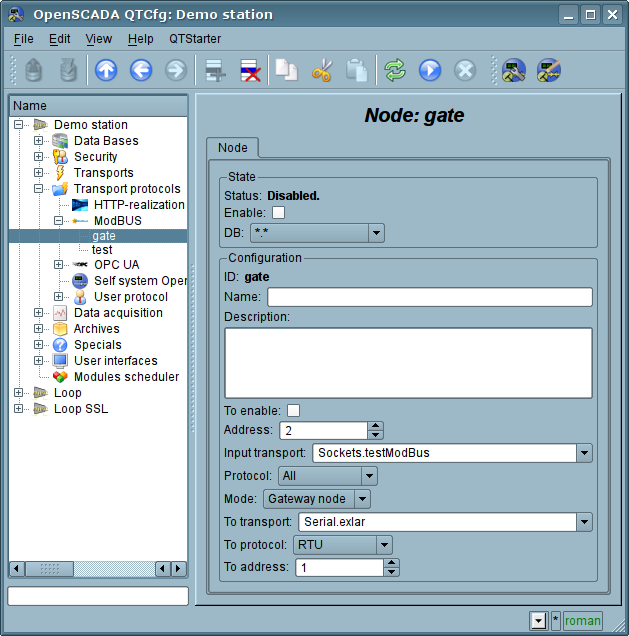
Fig.5. The tab "Node" of the configuration page of the node of the protocol in the "Gateway of the node" mode.
The mode of the node of the protocol "Gateway of the network"
Mode is used to carryover the requests of the network at whole to the other ModBus network from the ModBus network, in which this node is configured. Ie request to the device with any address will be sent to another network, without diverting. The overall configuration of the node is made in the tab "Node"(Fig. 6) by the parameters:
- The state of the node, as follows: «Enable» and the name of the database containing the configuration.
- Id, name and description of the node.
- The state, in which the node must be translated at boot: «To enable».
- Incoming transport of the network, from which the requests are transfered.It is selected from the list of input transport of the subsystem "Transports" of OpenSCADA.
- Variant of the ModBus protocol, requests in which must be processed by the node from the list: All, RTU, ASCII, TCP/IP.
- The choice of the mode, in this case the mode "Gateway of the network".
- Transport, in which the request must be redirected, from the list of outgoing transports of subsystem "Transports".
- Protocol in which to redirect the request.
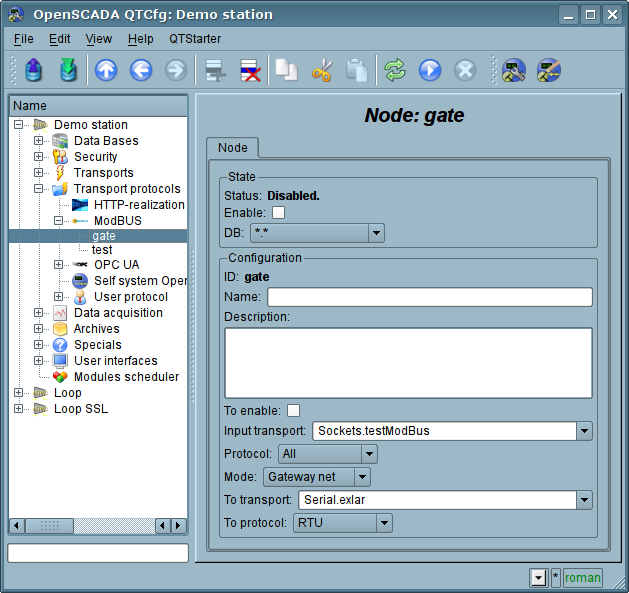
Fig.6. The tab "Node" of the configuration page of the node of the protocol in the "Gateway of the network" mode.
2.3 Report of the ModBus requests
To be able to monitor and to diagnosing the correct implementation of requests to the various components the a module provides an opportunity to incorporate the report of the requests that pass through the protocol module. The report included by indication of non zero number of entries in the tab "Report" of the page of the module of the protocol(Fig.7).
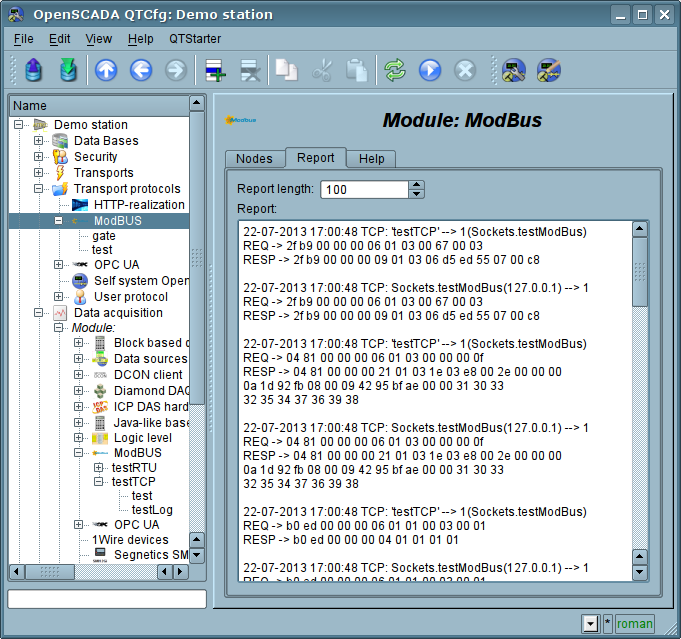
Fig.7. "Report" tab of the page of the module of the protocol.
3. Data acquisition module
The data acquisition module provides an opportunity to interrogate and write registers and bits of devices through protocol modes TCP, RTU, ASCII and commands of request 0x01 — 0x06, 0x0F, 0x10.
3.1. Controller of data
For addition of a ModBus data source the controller is created and configured in the system OpenSCADA. Example of the configuration tab of the controller is depicted in Fig.8.
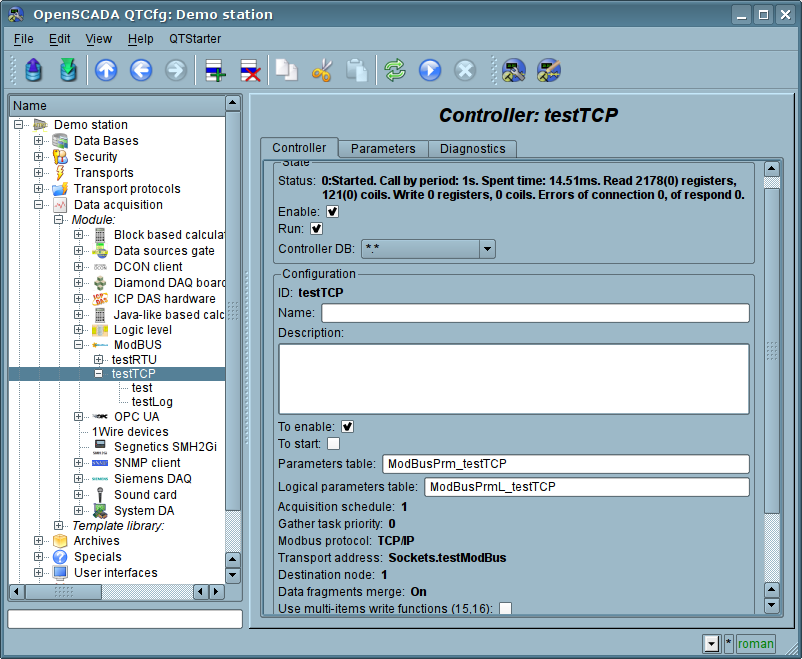
Fig.8. Configuration tab of the controller.
Using this tab you can set:
- The state of the controller, as follows: Status, «Enable», «Run» and the name of the database containing the configuration.
- Id, name and description of the controller.
- The state, in which the controller must be translated at boot: «To enable» and «To start».
- Names of tables to store the configuration of the parameters of the controller for standard and logical types.
- The acquisition schedule policy and the priority of the task of data acquisition.
- ModBus protocol, used for request to real device (TCP/IP, RTU or ASCII).
- Address of outbound transport from the list of configured outbound transports in the subsystem "Transports" of OpenSCADA.
- ModBus destination node. In the case of protocols RTU and ASCII this is the unique address of the physical device, and when TCP/IP — the identifier of the unity.
- Combining fragments of the registers. Standard functions 01-04 let to request at once multiple adjacent registers or bits. This strategy often allows to optimize the traffic and time. However, the required registers are not always located adjacent to each other, this option allows you to collect them in blocks of up to 100 registers, or 1600 bits.
 The installing of this parameter must be approached with caution, since not all devices support access to registers between fragments.
The installing of this parameter must be approached with caution, since not all devices support access to registers between fragments.
- Use multi-items write functions (0x0F,0x10). Instead one-item write will used multi-items functions.
- Connection timeout in milliseconds. Specifies the time interval during which the answer is expected. If there is zero waiting time by default the transport waiting time is used. Allows taking into account individual properties of the controller in the common network.
- Time of connection recovery in seconds. Specifies the time interval after which the re-attempt of the request to previously inaccessible device is done.
- Attempts of request for the protocols RTU and ASCII. Indicates the number of attempts by the repetition of the request in case of incomplete or damaged answer.
- Maximum request block size (bytes). Maximum size (bytes) of registers and coils blocks set. This usefull for controllers with like limits.
3.2. Parameters
Data acquisition module provides two types of parameter: "Standard"(std) and "logical"(logic). Additional configuration fields, the parameters of this module are:
- "Standard"(std):
- Attributes list — contains a structured list of configuration for the attributes ModBus.
- "logical"(logic):
- Parameter template — DAQ parameter's template address.
Standard parameter type(std)
Main page of configuration parameters of the standard type is shown in Figure 9.
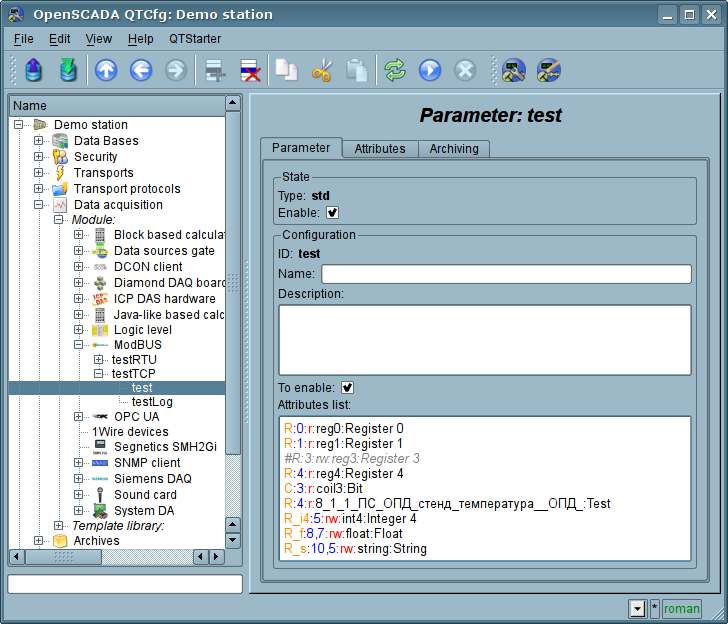
Fig.9. Configuration tab of the standard parameter type.
The structure of the attribute in the parameter list of attributes can be written as follows: "{dt}:{numb}:{rw}:{id}:{name}".
Where:
rw — read/write mode ("r"—read; "w"—write; "rw"—readwrite);
id — created attribute identifier;
name — created attribute name.
Examples:
"C:100:rw:var1:Variable 1" — coin access;
"R_f:200:r:float:Float" — get float from registers 200 and 201;
"R_i4:400,300:r:int32:Int32" — get int32 from registers 400 and 300;
"R_b10:25:r:rBit:Reg bit" — get bit 10 from register 25;
"R_s:15,20:r:str:Reg blk" — get string, registers block, from register 15 and size 20."
Line which start at symbol '#' is commentary and processing for it pass.
In accordance with a specified list of attributes interrogation and the creation of the attributes of the parameter is carried out(Figure 10).
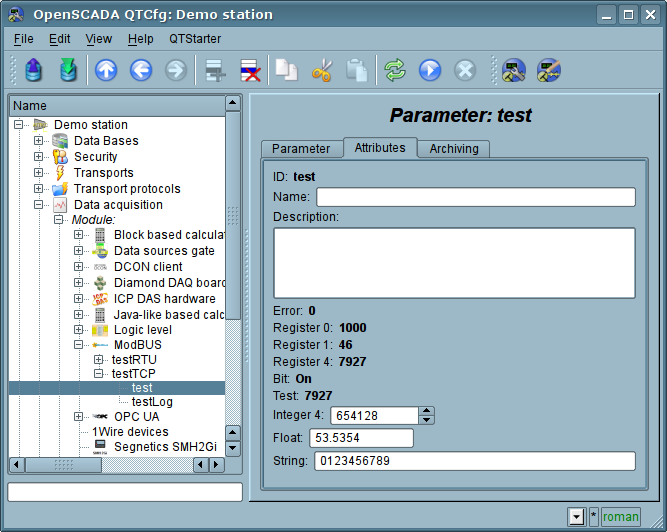
Fig.10. Tab of the attributes of the standard parameter type.
Logical parameter type(logic)
Main page of configuration parameters of the logical type is shown in Figure 11.
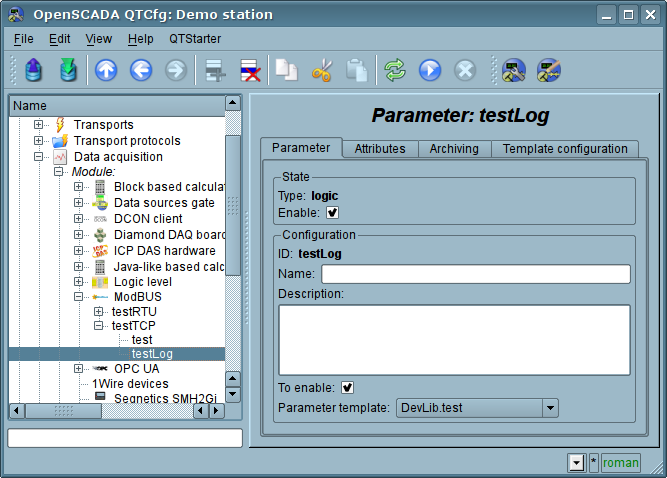
Ðèñ.11. Configuration tab of the logical parameter type.
When forming a template for the logical type of the parameter of the controller, do not take into account the reference format template, since it is not used and can be omitted. Same reference value, when configuring the the template (Fig. 12), written in the format: "{dt}:{numb}:{rw}".
Where:
"R" and "RI" can be expanded by suffixes: "i2"—Int16, "i4"—Int32, "i8"—Int64, "u2"—UInt16, "u4"—UInt32, "f"—Float, "d"—Double, "b5"—Bit5, "s"—String (size by default is 10 and up to 100 registers);
numb — ModBus device's data address (decimal, hexadecimal or octal) [0...65535];
rw — read/write mode ("r"—read; "w"—write; "rw"—readwrite).
Examples:
"C:100:rw" — coin access;
"R_f:200:r" — get float from registers 200 and 201;
"R_i4:400,300:r" — get int32 from registers 400 and 300;
"R_b10:25:r" — get bit 10 from register 25;
"R_s:15,20:r" — get string, registers block, from register 15 and size 20.
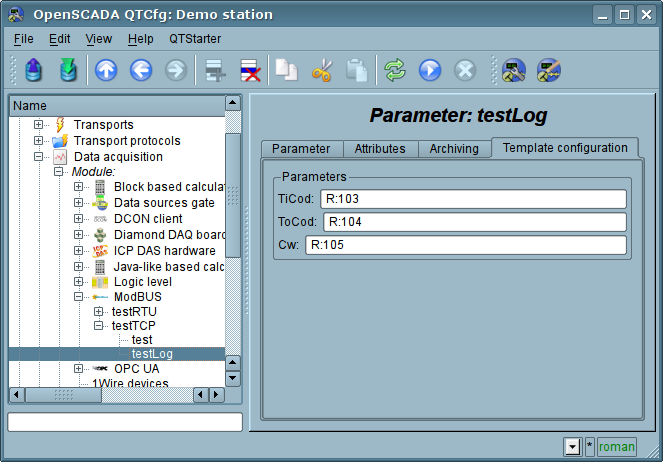
Ðèñ.12. Tab "Template configuration" of the logical parameter type.
The module provides a special treatment of a number of attributes of the template:
- f_frq — Frequency computation procedure template, or the time after the last calculation, the negative, in seconds, for scheduling of CRON, read-only.
- f_start — First calculate of template's procedure, start, read-only.
- f_stop — Last calculate of template's procedure, stop, read-only.
- f_err — The parameter error, full access. Value of the attribute is set to the parameter's error attribute "err".
- SHIFR — The parameter code, read-only.
- NAME — The parameter name, read-only.
- DESCR — The parameter description, read-only.
- this — The parameter object, allow access to attributes of the parameter, for example to their archives access.
In accordance with the pattern underlying parameter, we get a set of attributes of the parameter Fig.13.
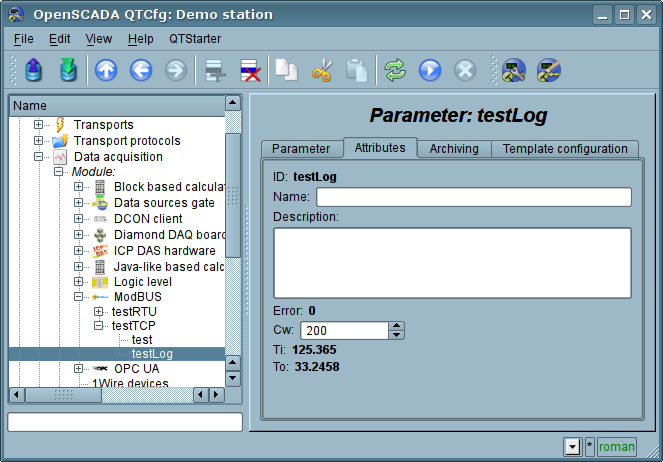
Fig.13. Tab of the attributes of the logical parameter type.
3.3. User programming API
In view of the module support logical type parameters make sense to provide a number of functions the user API to call from a template of logical parameter.
The object "Controller" [this.cntr()]
- string messIO(string pdu) — sending pdu through the transport of controller object by means of ModBus protocol. PDU query result is placed instead of the query pdu, and the error returned by the function.
The object "Parameter" [this]
- bool attrAdd( string id, string name, string tp = "real", string selValsNms = "" ) [for enabled parameter of the logical type] — attribute id and name for type tp add. If the attribute already present then will apply properties allowed to hot changing: name, selection mode and the selection mode parameters.
- id, name — new attribute id and name;
- tp — attribute type [boolean | integer | real | string | text | object] + selection mode [sel | seled] + read-only [ro];
- selValsNms — two lines with values in first and it's names in first (separated by ";").
- bool attrDel( string id ) [for enabled parameter of the logical type] — attribute id remove.
Links