Module of subsystem "Archives" <DBArch>
| Module: | DBArch |
| Name: | Arhivator on the DB |
| Type: | Archive |
| Source: | arh_DBArch.so |
| Version: | 1.2.0 |
| Author: | Roman Savochenko, Maxim Lysenko (2009) |
| Description: | The archiver module. Provides functions for messages and values archiving to DB. |
| License: | GPL |
Introduction
The module is designed for archiving messages and values of OpenSCADA to a database maintained by OpenSCADA.
Any SCADA system provides the ability to archive the collected data, i.e. formation of history of the changes (dynamics) of processes. Archives conditionally can be divided into two types: archives of messages and archives of values.
A feature of the archives of messages is that so-called events are archived. The characteristic feature of the events is its time of occurrence. The archives of messages are usually used for archiving ,messages in the system, i.e.
conducting of logs and reports. Depending on the source the messages can be classified according to different criteria. For example, this may be the reports of emergency situations, the reports of actions of the operators,
reports of the glitches of connection and others.
A feature of the archives of values is their frequency, measured in the time lag between two adjacent values. Archives of values are used for archiving the history of continuous processes. As the process is continuous, it can only be archived by introducing the notion of quantization of time interviewing, because otherwise we get the archives of infinite dimensions in view of continuity of the nature of the process. In addition, practically, we can get value from the time limited by the data sources. For example, a fairly high-quality data sources in the industry, are rarely allowed to receive data at a frequency of more than 1kHz. And this is without taking into account of the sensors themselves, which have even less qualitative characteristics.
For conducting of archives in the system OpenSCADA the subsystem «Archives» is provided. This subsystem, according to the types of archives, consists of two parts: an archives of messages and archives of values. The subsystem, in general, is a module that allows you to create archives based on the different nature and methods of storing of data. This module provides a mechanism for the archiving on the file system for both: for the flow of messages, and for the flow of values.
1. Message Archiver
Archives of messages are formed by archiver. There can be the set of archivers, with individual settings, allowing to share archiving of different classes of messages.
The archiver of messages of this module stores data in a database table, which is named by the following way: "DBAMsg_{ArchID}". Where:
- ArchID — archiver identifier.
Module provides additional settings for the archiving process (Fig. 1).
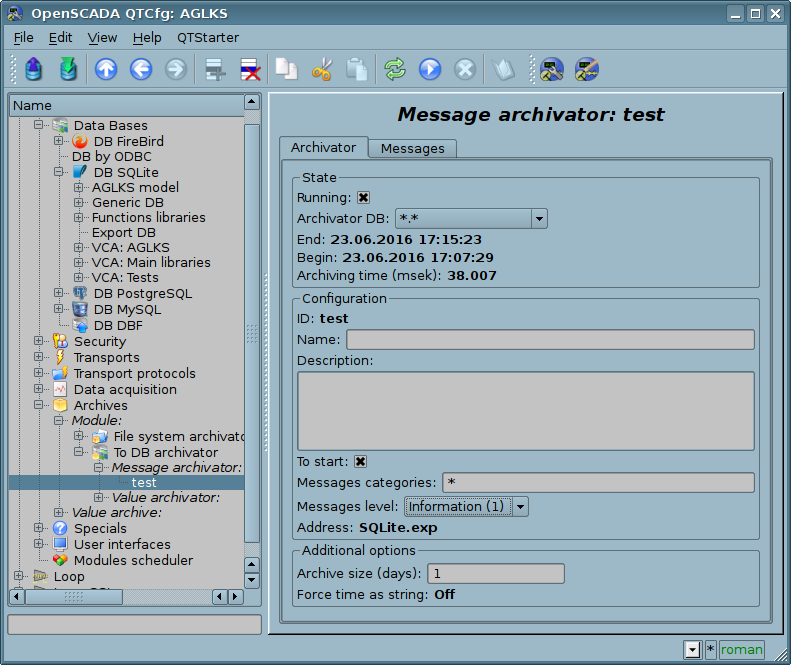
Fig.1. Additional settings of an archiving process of messages.
Those parameters represents by:
- Archive size (days) — determines the size of the archive over time. After exceeding the limit the old records will be deleted! Set to 0 for the limit disable and some performance rise.
- Force time as string — store messages time in the readable form. Only for DBs it supports by a specific data type like to "datetime" into MySQL.
Table of the database archiver has the following structure: {MIN,TM, TMU, CATEG, MESS, LEV}. Where:
- MIN — UTC time, in minutes, uses on reading by minutes, to rapid.
- TM — UTC time of the message, seconds from (01.01.1970). In the DB, containing a specialized type of storage date and time, can be used this specialized type, for the option "Force time as string".
- TMU — microseconds of time.
- CATEG — message category.
- MESS — text of the message.
- LEV — level of the message.
2. Values Archiver
Archives of values are formed particularly by archivers of the values for each registered archive. There can be a lot of archivers with individual settings that allow to divide the archives by various parameters, such as the accuracy and depth.
Archive of values is an independent component, which includes buffer processed by archivers. The main parameter of archive of value is a source of data. As a source of data may make the attributes of the parameters of subsystem "Data acquisition", as well as other external data sources (passive mode). Other sources of data could be: network archivers of remote OpenSCADA systems, environment of programming of systems OpenSCADA etc. No less important parameters are the parameters of the archive buffer. From the parameters of the buffer the opportunity of working of archivers depends on. Thus, the frequency of values in the buffer should be no more than the frequency of the fastest archiver, a buffer size not less than double the amount for the slowest archiver. Otherwise, the possible loss of data!
The overall scheme of archival of values vividly depicted in Fig. 2.
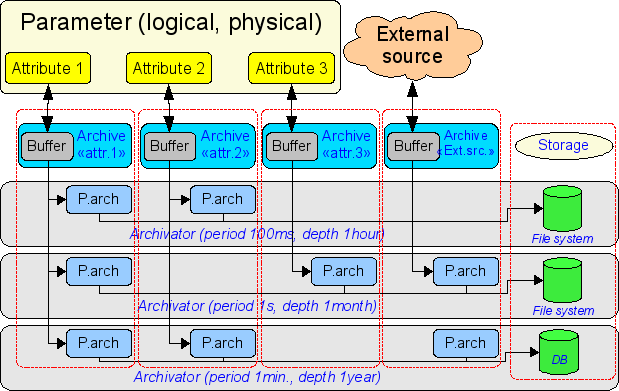
Fig.2. The overall scheme of the process of archiving by module DBArch.
Archive of this module stores data in a database table, which is called by the following way: "DBAVl_{ArchID}_{ArchiveID}". Where:
- ArchID — identifier of the archiver of values.
- ArchiveID — identifier of the archive.
Module provides additional settings for the archiving process (Fig. 3).
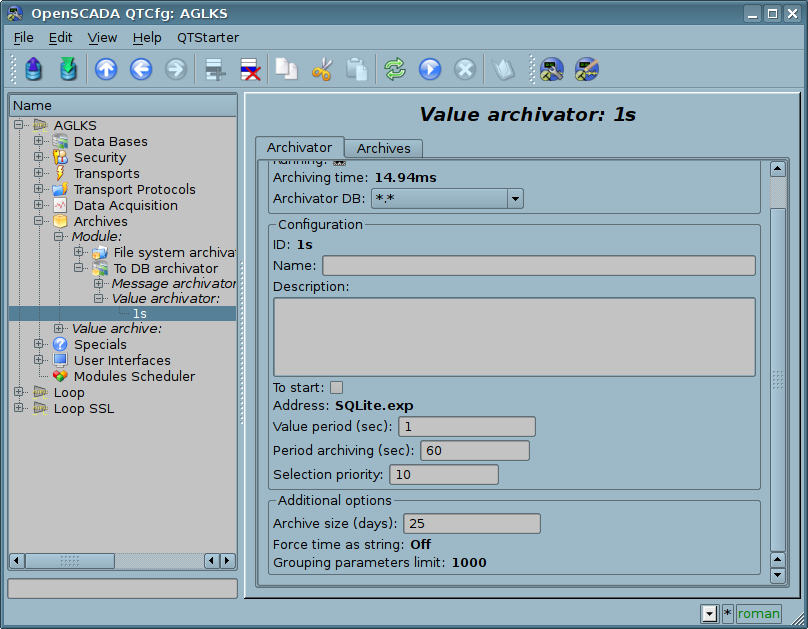
Fig.3. Additional settings of an archiving process of values.
Those parameters represents by:
- Archive size (hours) — determines the size of the archive over time. After exceeding the limit the old records will be deleted! Set to 0 for the limit disable and some performance rise.
- Force time as string — store values time in the readable form. Only for DBs it supports by a specific data type like to "datetime" into MySQL.
Table of database archiver of values is as follows: {TM, TMU, VAL). Where:
- TM — UTC time of the value, the second from (01.01.1970). In the databases, containing a specialized type of storage date and time, it can be used this type of specialization.
- TMU — Time value in microseconds.
- VAL — The value, type of value is determined by the type of the column (Integer, Real, String).
3. Informational table of the archival tables
To store the beginning, end and other information of archives in archival tables the informational table with the name of the module is created: "DBArch". This table has the structure: {TBL, BEGIN, END, PRM1, PRM2, PRM3).
Where:
- TBL — Name of the table of the archive.
- BEGIN — Beginning of data in the archive.
- END — End of data in the archive.
- PRM1 — Optional parameter 1.
- PRM2 — Optional parameter 2.
- PRM3 — Optional parameter 3.
4. Productivity and limits
Due to the specific of working with the DBMS and it's related low performance here also presented limits to the data access by the OpenSCADA DB abstraction. The abstraction means now using the seek API (SELECT by pointed single records) and by minutes. Into following table shown some practical results for different DBMS and it's configuration, for time limit into 5 seconds:
| Configuration | Seek limit, records | Seeks, read number limit | Notes |
| PostgreSQL, local, Intel Core I5 | 1500 | 10000 | Then maximum messages flow is 1500 messages per minute and maximum guaranty requested block is 7 days. |
Links