1. Functions of the system.
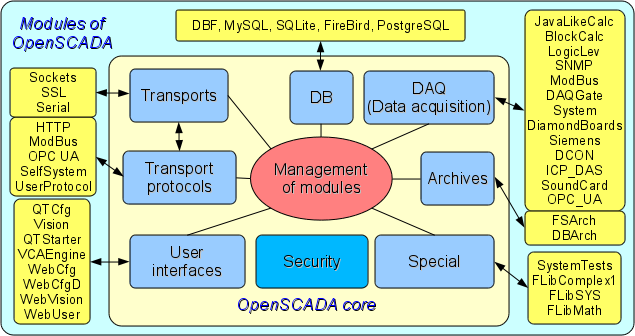
Fig. 1. The block scheme of OpenSCADA system
1.1. Modularity.
For giving flexibility and a high degree of scalability the OpenSCADA system is constructed by a modular principle. Close integration of modules with a kernel of system imposes the great responsibility on process of a writing of modules and enters an element of instability into the system, however owing to an opportunity of creation of the allocated configurations, this danger smooths out with preservation of a high degree of flexibility.
Modules of OpenSCADA system are stored in dynamic libraries. Each dynamic library can contain set of modules of various type. Filling of dynamic libraries by modules is determined by functional connectivity of modules. Dynamic libraries suppose hot replacement, that allows during functioning to update separate parts of system. The method of storage of a code of modules in dynamic libraries is the main for OpenSCADA as far as it is supported practically by all modern operational systems(OS). However it does not exclude an opportunity of development of other methods of storage of a code of modules.
On the basis of modules the following functional parts of OpenSCADA system are realized:
- databases;
- archives (messages and values);
- protocols of communication interfaces;
- communication interfaces, transports;
- sources of data and data acquisition;
- interfaces of the user (GUI, TUI, WebGUI, speech, signal...);
- the additional and special modules.
Management of modules is carried out by a subsystem "Management of modules". Functions of a subsystem are: connection, switching-off, updating of modules, and also other operations connected with modules and libraries of modules.
1.2. Subsystems.
Architecturally the OpenSCADA system shares on subsystems. Subsystems can be of two types: usual and modular. Modular subsystems possess the property of expansion by means of modules. Each modular subsystem can contain set of modular objects. For example the modular subsystem of "Database" contains modular objects of types of databases. The modular object is a root inside of the module.
In total the OpenSCADA system contains 9 subsystems from them 7 subsystems are modular. 9 subsystems of the OpenSCADA system are basic and are present at any configuration. To the list of 9 subsystems new subsystems by means of modules can be added. Subsystems of the OpenSCADA system:
- Archives (modular).
- Databases (modular).
- Safety.
- Interfaces of the user (modular).
- Management of modules.
- Data acquisition (modular).
- Transport protocols (modular).
- Special (modular).
- Transports (modular).
1.3. PLC and other sources of dynamic data. A subsystem "Data acquisition".
For support of sources of dynamic data, whether it be PLC-controllers, communication devices, virtual sources, etc., the subsystem "Data acquisition" is intended. Functions of this subsystem include granting the received data in the structured appearance and maintenance of management with these data, for example the updating of data.
The subsystem "Data acquisition" is modular and, as consequence, contains modular objects of types of sources of dynamic data. For example, for October 2007ã, the OpenSCADA system supports following types of sources of data:
- Cards of data acquisition from "Diamond systems".
- Data acquisition from operational systems (OS).
- the Block calculator.
- the Calculator in Java-like language.
- the Transporter of data of a subsystem "Data acquisition" from one OpenSCADA station to another.
- Access to logic controllers by means of the protocol "ModBUS".
- Data acquisition from network devices by means of protocol SNMP.
- The source of data of a logic level of OpenSCADA system.
- Access to highly intellectual logic controllers by means of MPI protocol and communication processor CIF50PB of Hilscher GMBH firm.
Each type of a source is made in the form of the separate module which can be connected/disconnected. Each type of a source can contain separate sources (controllers).
Separately taken controller can contain the parameters of certain by the module types. For example parameters of analog type: the basic information which they gives the value of the integer or real type is. Structurally, the parameter represents the list of attributes which are contained by data. Attributes can be of four base types: symbolical string (text), integer, real and logic type.
Structures of controllers, parameters and their types are contained in the subsystem "Data acquisition", and objects of modules carry out their filling according to own specificity.
The source of dynamic data can be remotes, i.e. connected on the remote OpenSCADA system. For communication with such sources of data the transport type of controllers (Transporter) is used. Function of the given type of a source of data is reflection of sources of data of remote OpenSCADA stations on local station.
1.4. Databases. A subsystem of "Database"
For a data storage of system databases (DB) are everywhere used. With a view of systematization of access and management of databases in OpenSCADA system the subsystem "Database" is provided. For support of various DB/DBMS the subsystem is modular.
In a role of the modular objects, containing in a subsystem, type DB/DBMS acts, i.e. the module of a subsystem "Database", which practically contains realization of access to the certain type of a DB. For example modules: DBF, MySQL, SQLite.
The object of type DB/DBMS, in its turn, contains the list of objects of separated DB of the given type. And the object of a DB contains the list of objects of tables which are contained by data in the tabulated form.
Practically all the data of OpenSCADA system are stored in this or that DB. The toolkit of system allows to transfer easily the data from one type of a DB on another and as consequence provide an optimum selection of DB type under the concrete area of OpenSCADA system. Transfer of the information from one DB to another can be made by two ways. The first is a change of the address of a working DB and save of all system on it, the second is a direct copying the information between DB. Except for copying the function of direct editing of contents of tables of a DB is supported also.
For the organization of the centralized access of the allocated system to a uniform DB two ways are provided. The first is using of network DBMS, for example MySQL. The second way is using of transport type of a DB on local systems for access to one central DB (It is planned.). Function of a transport DB is transfer of queries to a DB on remote OpenSCADA system.
Data can be stored also in a configuration file of system. The mechanism of full reflection of structure of a DB on structure of a configuration file is realized. I.e. the standard configuration can be placed in a configuration file. An essence of such mechanism that by default for example at start without a DB, it is possible to describe the data of system in a configuration file. In the further, these data can be redefined in a DB. Besides for cases of impossibility of start of any DB generally, it is possible to store all data in a configuration file.
For access to databases the mechanism of registration of a DB is used. Registered DB in system are accessible to all subsystems of OpenSCADA system and can be used in their work. Owing to this mechanism it is possible to provide an allocation of data storage. For example, various libraries can be stored and extend independently, and connection of library will consist in simple registration of the necessary DB.
In the further, realization of duplication of a DB by linkage of the registered DB is planned. This mechanism will allow to increase considerably reliability of OpenSCADA system as a whole by reservation of the mechanism of a data storage. (It is planned.)
1.5. Archives. A subsystem "Archives".
Any SCADA system gives an opportunity of archiving the acquisition data, i.e. formation of history of change (dynamics) of processes. Archives, conditionally, it is possible to divide into two types: archives of messages and archives of values.
Feature of archives of messages is that the subject of archiving are, so-called, events. A characteristic attribute of event is time of occurrence of this event. Archives of messages, usually, are used for archiving messages in system, i.e. conducting logs and reports. Depending on a source, messages can be classified by various criteria. For example, it can be reports of emergencies, reports of actions of operators, reports of failures of connection, etc.
Feature of archives of values is their periodicity defined by the time interval between two adjacent values. Archives of values are applied for archiving of history of continuous processes. As far as process is continuous and it's archiving is possible only by introduction of conception of quantization of interrogation of values as differently we receive archives of the infinite sizes, in view of a continuity of the nature of process. Besides, practically, we can receive values with the period limited by sources of data. For example, qualitative enough sources of data, in the industry, data with frequency more 1kHz seldom allow to obtain. And it without taking into account sensors having even less qualitative characteristics.
For the decision of tasks of archiving data flows in OpenSCADA system the subsystem "Archives" is provided. The subsystem "Archives" allows to conduct both: archives of messages and archives of values. The subsystem "Archives" is modular. The modular object containing in a subsystem "Archives" the type of the archiver acts. The type of the archiver defines the way of a data storage, i.e. storehouse (file system, DBMS, a network, etc.). Each module of a subsystem "Archives" can realize both: archiving of messages, and archiving of values. The subsystem "Archives" can contain set of the archives served by various modules of a subsystem.
The message in OpenSCADA system is characterized: by date, by level of importance, by category and the text of the message. Date of the message specifies for the period of creation of the message. The level of importance specifies a degree of importance of the message. The category determines the address or the conditional identifier of a source of the message. Usually, the category contains a full way to a source of the message in system. The text of the message, actually, also carries meaning content of the message.
During archiving messages are passed through the filter. The filter works on a level of importance and a category of the message. The level of the message in the filter specifies that it is necessary to pass messages with specified or higher level of importance. To filtering on a category templates are used, which define what messages are applied to pass. Each archiver contains own options of the filter. Consequently it is possible to create easily various specialized archivers for archive of messages. For example archivers of messages it is possible to dedicate on:
- logs for storage of the debugging information and other working information of a server;
- various reports (the report of actions of clients, the report of infringements and exceptions, the report of events...).
The archive of values in system OpenSCADA acts as an independent component which includes the buffer processable by archivers. Key parameter of archive of value is the source of data. In a role of a source of data attributes of parameters of OpenSCADA system and also other external sources of data (a passive mode) can act. Other sources of data can be: network archivers from remote OpenSCADA systems, the environment of programming of OpenSCADA system, etc.
Key component of archiving of values of continuous processes is the buffer of values. The buffer of values is intended for intermediate storage of a file of the values received with certain periodicity (quantum of time). The buffer of values is used as for direct storage of big arrays of values in archives of values, before direct "retire" on physical carriers, and for manipulations with the staff of values, i.e. in functions of rame-accurate query of values and their placement in buffers of archives.
For the organization of the dedicated archivers, in the allocated systems it is possible to use transport type of the archiver (It is planned.). Function of transport type of the archiver is reflection of the remote central archiver on local system. As consequence, archivers of transport type carry out data transmission between local system and the archiver of the remote system, hiding from subsystems of local system the real nature of the archiver.
1.6. Communications. Subsystems "Transports" and "Transport protocols".
As far as the OpenSCADA system is pawned as is high-scaled system that support of communications should be flexible enough. For satisfaction of a high degree of flexibility, communications in OpenSCADA system are realized in subsystems "Transports" and "Transport protocols" which are modular.
The subsystem "Transports" is intended for an exchange of the not structured data between OpenSCADA system and external systems. In a role of external systems can act even remote OpenSCADA systems. Not structured data are understood as a file of symbols of the certain length. The modular object containing in a subsystem "Transports", the type of transport acts. The type of transport defines the mechanism of transfer of not structured data. For example it can be:
- sockets (TCP/UDP/UNIX);
- channels;
- shared memory.
The subsystem "Transports" includes support of input and output transports. Input transport is intended for service of external queries and sending of answers. Output transport, on the contrary, is intended for sending messages and expectation of the answer. Consequently, input transport contains a configuration of the given station as server, and output transport contains a configuration of the remote server. The module of a subsystem "Transports" realizes support both: input and output transports.
The subsystem "Transport protocols" is intended for structuring of data received from a subsystem "Transports". As a matter of fact, the subsystem "Transport protocols" is continuation of a subsystem "Transports" and carries out functions of check of structure and integrity of the received data. So, for the indication of the protocol together with which transport should work, the special configuration field is provided. The modular object containing in a subsystem "Protocols" is the protocol. For example, transport protocols can be:
- HTTP (Hyper Text Transfer Protocol);
- SelfSystem (OpenSCADA the system protocol).
The full chain of connection can be written down as follows:
- the message is transferred in transport;
- transport transfers the message to the protocol, connected with it, by creation of new object of the protocol;
- the protocol checks integrity of data;
- if all data have come, transport must be informed about the termination of expectation of data and to transfer it the answer, differently to inform, that it is necessary to expect still;
- transport, having received {confirmation, sends the answer and delete object of the protocol;
- if confirmations are not present, the transport continues expectation of data, and in the case of their receipt transfers them to the saved object of the protocol.
Protocols for output transports are supported also. The output protocol incurs function of dialogue with transport and realization of features of the protocol. The internal side of access to the protocol is realized by data-flow way with own structure for each protocol module. Such mechanism allows to carry out transparent access to external system, by means of transport, simply specifying a name of the protocol by means of which to serve transfer.
Owing to standard API-access to transports of OpenSCADA system it is possible to change easily a way of data exchange not touching exchanging systems. For example, in the case of a local exchange it is possible to use faster transport on the basis of shared memory, and in the case of an exchange through the Internet and a local network to use TCP or UDP sockets.
1.7. Interfaces of the user. A subsystem "Interfaces of the user".
SCADA-systems as a class, assume presence of user interfaces. In OpenSCADA, for granting the user interfaces, the subsystem "The user interfaces" is provided. The user interface of OpenSCADA system is understood not only as the environment of visualization from which the end user should work, but also as everything, that concerns the user, for example:
- environments of visualization;
- configurators;
- alarming and signaling devices.
The subsystem "The user interfaces" is modular. As modular object of a subsystem the concrete interface of the user actually acts. Modularity of subsystem allows to create various interfaces of users on various GUI/TUI libraries and to use optimal of decisions in particularly taken case, for example, for environments of performance of programmed logic controllers it is possible to use configurators and visualizers on the basis of Web-technologies (WebCfg, WebUI), and in case of stationary workstations to use the same configurators and visualizers, but on the basis of libraries QT, GTK.
1.8. Security of system. A subsystem "Security".
The OpenSCADA system is the branched out system which consists of ten subsystems and can include set of modules. Consequently, granting of unlimited access by all to these resources is at least unsafe. Therefore, for differentiation of access in OpenSCADA system, the subsystem of "Security" is provided. The basic functions of a subsystem "Security" are:
- storage of registration records of users and groups of users;
- authentication of users;
- check of access rights of the user to this or that resource.
1.9. Management of libraries of modules and modules. A subsystem "Management of modules".
The OpenSCADA system is constructed by a modular principle that means presence of set of modules with which it is necessary to operate. For performance of function of management by modules of OpenSCADA system the subsystem "Management of modules" is provided. All modules, for the present moment are delivered in system by means of shared libraries (containers). Each container can contain set of modules of various type.
The subsystem "Management of modules" realizes the control over the status of containers and allows to carry out hot addition, removal and updating of containers and modules containing in them.
1.10. Unforeseen opportunities. A subsystem "Special".
Certainly, to provide all probable functions it is impossible, therefore in OpenSCADA system the subsystem "Special" is provided. The subsystem "Special" is modular and is intended for addition in OpenSCADA system unforeseen functions by modular expansion. For example, by means of a subsystem "Special" can be realized:
- tests of OpenSCADA system and its modules;
- libraries of functions of the user programming.
1.11. The user functions. Objective model and the environment of programming of system.
Any modern SCADA system should contain the mechanisms giving an opportunity to program at the user level, i.e. to contain the environment of programming. The OpenSCADA system contains such environment. By means of the environment of programming of OpenSCADA system it is possible to realize:
- Algorithms of management of technological processes.
- Large dynamic models of real time of technological, chemical, physical and other processes.
- Adaptive mechanisms of management on models.
- The user procedures of management by internal functions of system, its subsystems and modules.
- Flexible formations of structures of parameters at a level of the user, with the purpose of creation of parameters of non-standard structure and its filling on algorithm of the user.
- Auxiliary calculations.
The environment of programming of OpenSCADA system represents a complex of assets organizing the computing environment of the user. Into structure of a complex of assets are included:
- objective model of OpenSCADA system;
- modules of libraries of functions;
- computing controllers of a subsystem "Data acquisition" and other calculators.
Modules of libraries of functions give set of functions of the certain orientation expanding objective model of system. Libraries can be realized both: by the set of functions of the fixed type, and functions supposing free updating and addition.
Libraries of functions of the fixed type can be given by standard modules of system, organically supplementing objective model. Functions of such libraries will represent the interface of access to assets of the module at a level of the user. For example, "The environment of visual data presentation" can give functions for delivery of various messages. Using these functions the user can realize interactive algorithms of communication with system.
Libraries of functions of free type give the environment of a writing of the user functions on one of programming languages. Within the limits of the module of libraries of functions mechanisms of creation of libraries of functions can be given. So, it is possible to create libraries of devices of technological processes, and in a consequence to use them by linkage. Various modules of libraries of functions can give realizations of various programming languages.
On the basis of the functions given by objective model, computing controllers are under construction. Computing controllers carry out linkage of functions with parameters of system and the mechanism of calculation.