The module of subsystem "Data acquisition" <DiamondBoards>
| Module: | DiamondBoards |
| Name: | Diamond cards of data acquisition |
| Type: | DAQ |
| Source: | daq_DiamondBoards.so |
| Version: | 2.1.0 |
| Author: | Roman Savochenko, Maxim Lysenko (2009) |
| Description: | Provides an access to " |
| License: | GPL |
Introduction
The module provides for the system OpenSCADA support of dynamic data sources, based on the cards for data acquisition of Diamond Systems company (![]() http://diamondsystems.com). The module based on the universal driver of the manufacturer of the boards. Universal driver is available for almost all known software platforms in the form of a library. Universal driver has been received at
http://diamondsystems.com). The module based on the universal driver of the manufacturer of the boards. Universal driver is available for almost all known software platforms in the form of a library. Universal driver has been received at ![]() http://www.diamondsystems.com/support/software and it was included in the distribution kit of OpenSCADA, therefore, for the building of the module external libraries are not required. You need only an assembling of the Linux kernel module "dscudkp.ko" for working by interrupts and with FIFO.
http://www.diamondsystems.com/support/software and it was included in the distribution kit of OpenSCADA, therefore, for the building of the module external libraries are not required. You need only an assembling of the Linux kernel module "dscudkp.ko" for working by interrupts and with FIFO.
The boards of data acquisition of Diamond Systems represent the modules of expansion of the PC/104 form-factor. Boards may include: analog IO (input/outputs), digital IO, and counters. Complete set of cards can vary greatly. There can be contained only one type of IO or some mix. In addition, the function of data acquisition can be given to the system boards of this company. For example, the motherboard "![]() Athena" contains: 16 AI, 4 AO, 24 DIO.
Athena" contains: 16 AI, 4 AO, 24 DIO.
The module provides support for analog and digital IO into synchronous and asynchronous access modes. Analog inputs (AI) acquisition supports also into an interruption mode (by FIFO assistance). The method of the acquisition on interruption allows to achieve maximum frequency of interrogation which it is supported by the hardware. In the case of "Athena" system board the frequency achieves 100 kHz. In acquisition on interruption process the data becomes by packages of the main acquisition period and places into an archives buffer.
1. Data controller's object
On the controller's object level creates generic task for all board-parameters processing. Example of the tab of configuration of the controller's object shown in Figure 1.
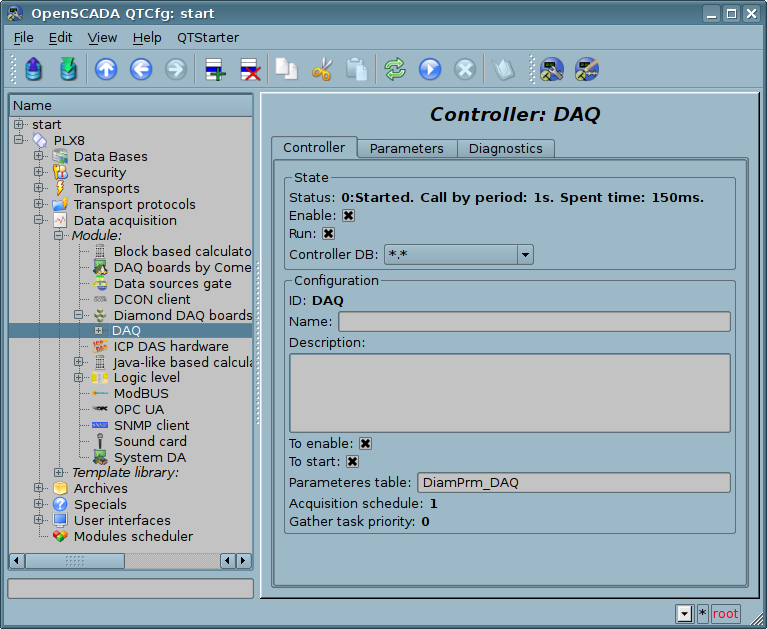
Fig.1. Tab of configuration of the controller's object.
In assistance with the tab you can set:
- The controller status, that is: state, states "Enabled" and "Started" and DB name with the configuration.
- Identifier, name and description of the controller's object.
- Status, in which the controller is to be switched at the boot time: "Enabled" and "Started".
- The table name for storing here of the controller's parameters configuration.
- Data acquisition task's scheduling policy and execution priority.
2. Parameter-board's object
A parameter-board's object same has a configuration of concrete board and provides available on the board data by attributes. Example of the tab "Parameter", configuration of the parameter-board at all, shown on Figure 2, and the tab "Configuration", signals properties, shown on Figure 3.
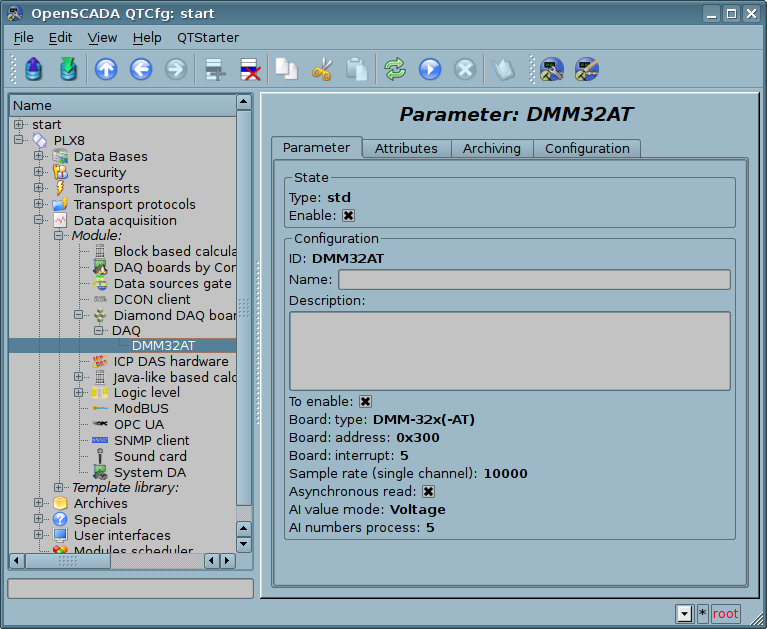
Fig.2. Tab "Parameter" of configuration of the parameter-board at all.
In assistance with the tab you can set:
- The parameter status, that is: type and status "Enabled".
- Identifier, name and description of the parameter's object.
- Status, in which the parameter is to be switched at the boot time: "Enabled".
- Type, address and vector of interruption of the board. The interruption vector allowed only for boards with the analog inputs and FIFO.
- Samplerate to single channel on the analog inputs acquisition by interrupt. Allowed only for boards with analog inputs and FIFO. Nonzero and correct value into this and previous field will enable the AI acquisition mode by interruption.
- Asynchronous reading mode, on the controller's object period. Working also into the AI acquisition mode by interruptions for discrete signals.
- Analog input values display mode: "ADC code (integer)", "Percent of the signal range (real)" and "Voltage (real)". The mode "Voltage" can not by allowed for all boards!
- Limit of analog parameters number in the processing. Useful for using lesser the channels number but frequently. Especially into the acquisition by interruptions mode and channel mode SE(single-ended) and "Differential" control.
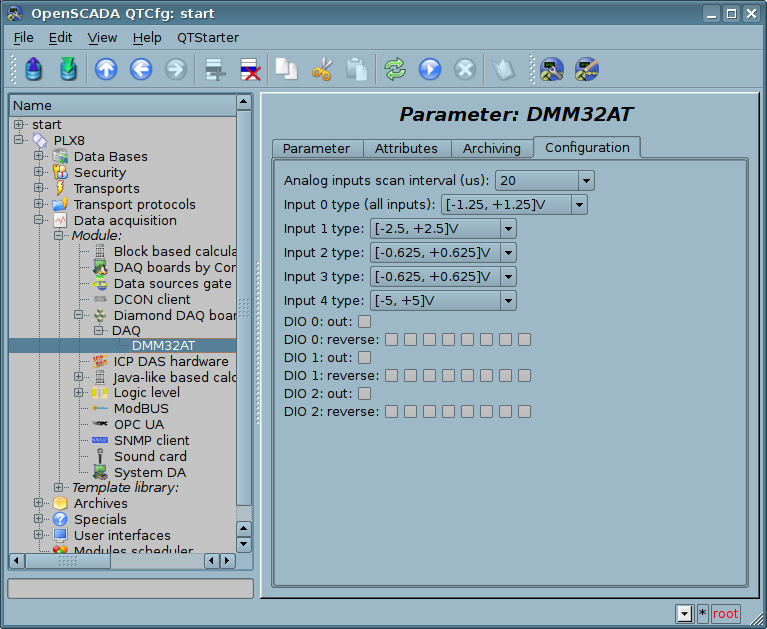
Fig.3. Tab "Configuration" of the signal's properties.
In assistance with the tab you can set:
- Analog inputs scan interval, it defines time between samples into the AI acquisition by interruption mode.
- AI range configuration. Into the AI acquisition mode by interruptions uses a range from the zero input why into the brackets we see "(all inputs)".
- Groups of discrete inputs (channels) direction for DIO and an inversion mode of concrete discrete inputs.
On the Figure 4 shown an example of tab "Attributes" for board "DMM-32x-AT".
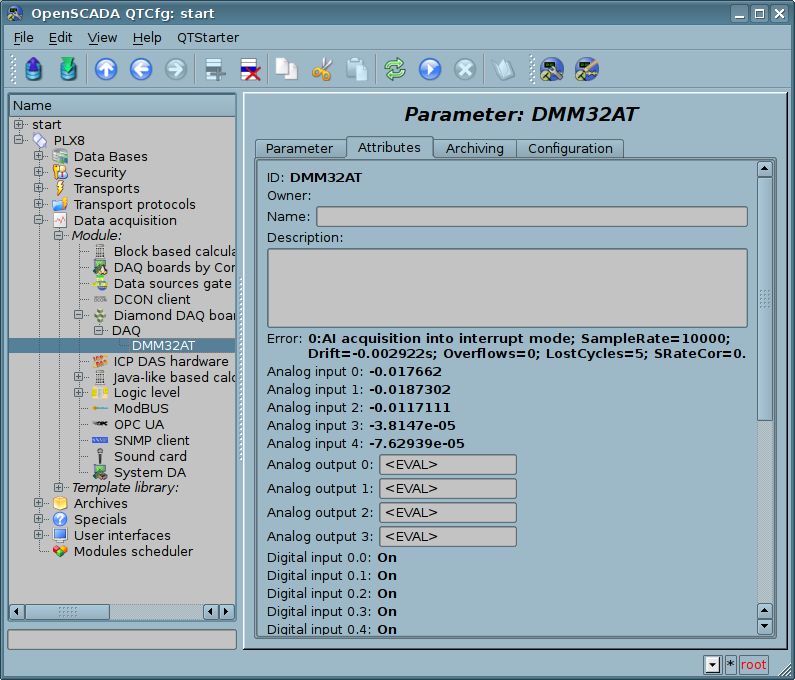
Fig.4. Tab "Attributes" of a parameter-board.
Into the table 1 shown a list of boards of firm "Diamond Systems", their support status and testing.
Table 1 Properties of firm "Diamond Systems" boards
| Board | AI (16 bit) | AO (12 bit) | DIO (x8) | DI (x8) | DO (x8) | Notes |
| DMM-16 | 16 | 4 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| Ruby-MM | 0 | 8 | 3 | 0 | 0 | |
| Opal-MM | 0 | 0 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| DMM | 16 (12 bit) | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| Pearl-MM | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 2 | |
| Onyx-MM | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 | |
| Ruby-MM-416 | 0 | 4 (16 bit) | 2 | 0 | 0 | |
| DMM-AT | 16 (12 bit, 100 kHz, 512 FIFO) | 2 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| DMM-16-AT | 16 (100 kHz, 512 FIFO) | 4 | 0 | 1 | 1 | |
| IR104 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 3 | 3 | |
| Prometheus | 16 (100 kHz, 48 FIFO) | 4 | 3 | 0 | 0 | |
| Hercules EBX | 32 (250 kHz, 2048 FIFO) | 4 | 5 | 0 | 0 | |
| Onyx-MM-DIO | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 | |
| Mercator | 0 | 0 | 3 | 0 | 0 | |
| Athena | 16 (100 kHz, 48 FIFO) | 4 | 3 | 0 | 0 | Verified |
| DMM-32x(-AT) | 32 (250 kHz, 1024 FIFO) | 4 | 3 | 0 | 0 | |
| GPIO-MM-11[12](DIO) | 0 | 0 | 6 | 0 | 0 | |
| GPIO-MM-21 | 0 | 0 | 12 | 0 | 0 | |
| Poseidon | 32 (250 kHz, 1024 FIFO) | 4 | 3 | 0 | 0 | |
| Athena-II | 16 (100 kHz, 2048 FIFO) | 4 | 3 | 0 | 0 | |
| DMM-32dx(-AT) | 32 (250 kHz, 1024 FIFO) | 4 | 3 | 0 | 0 | Verified |
| Helios | 16 (100 kHz, 2048 FIFO) | 4 | 5 | 0 | 0 | |
| Neptune | 32 (250 kHz, 1024 FIFO) | 4 | 4 | 0 | 0 |
Notes
Specific in operation by the AI acquisition by interrupts is the channels switching sync; measuring by different, external, counter and using FIFO for intermediate measuring buffer. Sure, this counter will different to some value from the real-time clock and the FIFO need to be have time to it reading. Course it is need to adjust-calibrate the data receipts with the real-time clock. At all implemented next mechanisms of the counters walk difference and other effects:
- FIFO overflow — as result here lost one data frame of FIFO size and performed channels shifting into the data area, at unaligned FIFO size to the channels number, addition to the block size alignment.
- Cycles lost — the processing data blocks task calling can be happen through one or several cycles, as result of a low priority and other effects. As result of the effect is overflow (wrapping) of the measuring data blocks and we need to reset the data time to the real-time.
- Difference into the measurement counter walk and the real-time clock — compensated by tune the real measurement samplerate to size of the time deviation more to one cycle of the processing. An error to the calling time and hitting to the buffer's part dropping border here presents, (transfers threshold) with the value about the dropping buffer's part size it is a half from the measurement period.
Links
Used version the Linux driver from Diamond systems: ![]() dscud5.91linux.tar.gz
dscud5.91linux.tar.gz
The patch for build driver at kernel Linux 2.6.29, used for data gathering by interrupt: ![]() lastkernels.patch
lastkernels.patch