Dynamic model of the steam boiler #9 of DMK
| Name: ModelKotelDMK Start: January 2007 State: Finished, August 2010 Participants: Roman Savochenko, Maxim Lysenko, Ksenia Yashina Description: The project is targeted to creating a complete dynamic model of a steam boiler ¹ 9 of Dnepr Metallurgical Combine (DMC). Address: Current DB into Live execution: | 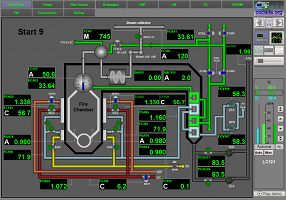 |
Introduction
The modelling object of this project for creation the full-scale real time dynamic model is multi-fuel steam boiler ¹9 of the Dnepr Metallurgical Combine (DMC). The distinctive feature of the boiler is its multi-fuel nature and the following features in optimal control of boiler's loading.
1 Purpose
Functionally, the purpose of the development is creation of the real time model of multi-fuel boiler.
Operational purpose of development is:
- ASC TP control algorithms' testing;
- SCADA-system algorithms' adequate functionality testing;
- Education of the technology staff.
2 Development
In order to speed up the development, use the experience of previous developments, as well as to improve the technology and development tools of the complete dynamic real-time models the decision to build the model in the OpenSCADA environment was made. The OpenSCADA system has the powerful mechanism of user side programming, as well as achievements to create a complete real-time dynamic models, which allow you to quickly create large real-time dynamic models. It was discussed in the paper ![]() report (RU) at 5
report (RU) at 5 ![]() 5 Ukrainian conference of developers and users of free software.
5 Ukrainian conference of developers and users of free software.
2.1 Technological process
Before the creation the model of the boiler the schematic diagram of the technological process model was formed, based on the schematic diagram of the real process. The scheme is shown in Fig. 1.
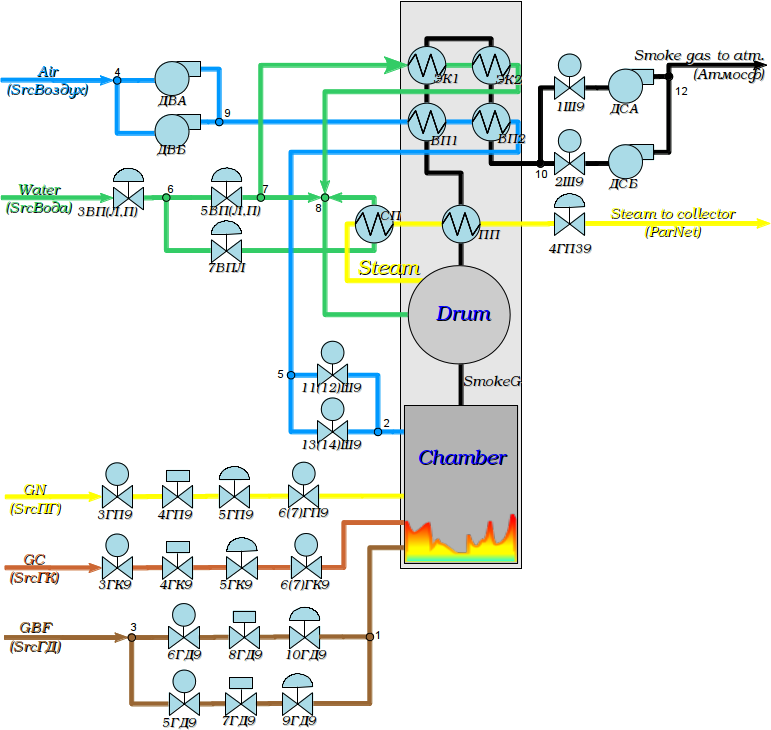
Fig. 1. The boiler DMK #9 technological scheme.
2.2 Modeling
For the construction of process model based on the available apparatus' models the original schematic diagram and block calculator (BlockCalc) of the OpenSCADA system were directly used. Apparatus models of the schematic diagram were appended to the block scheme in accordance with the schematic diagram. Part of the blocks were been added to the auxiliary equipment, as well as for the flows' nodes. Nodes' blocks numbers are indicated on the schematic diagram by numbers near the flows' nodes.
The model is made as the two block schemes of the block calculator. Content and properties of block schemes are shown in Table 1.
Table 1. The model's block schemes
| ID | Name | Target | Execution period (ms) | Execution time at Athlon 64 3000+ (ms) |
| kotel9 | DMC Boiler9 | Contains a model of boiler ¹ 9 Dnepr Metallurgical Combine. | 5 | 1.1 |
| kotel9_cntr | DMC Boiler9 Controller | Contains a model of the boiler's control system. | 1000 | 0.05 |
From the characteristics of block diagrams you can see that the resource intensity of the overall model to the CPU Athlon 64 3000 + (2000MHz) is 22%.
Table 2 lists the apparatus models being used in accordance with the schematic diagram.
Table 2. The used apparatus models
| Apparatus model | Devices (model blocks) |
| Library "Technological devices (DAQ.JavaLikeCalc.techApp)" | |
| Boiler: barrel (boilerBarrel) | kotel9.Áàðàáàí |
| Boiler: burner (boilerBurner) | kotel9.Òîïêà |
| Gas compressor (compressor) | kotel9.ÄÑÀ, kotel9.ÄÑÁ, kotel9.ÄÂÀ, kotel9.ÄÂÁ |
| Heat exchanger (heatExch) | kotel9.ÏÏ, kotel9.ÂÏ1, kotel9.ÂÏ2, kotel9.ÑÏ, kotel9.ÝÊ1, kotel9.ÝÊ2 |
| Valve (klap) | kotel9.3ÂÏ, kotel9.5ÂÏ, kotel9.7ÂÏ, kotel9.5ÃÄ9, kotel9.6ÃÄ9, kotel9.7ÃÄ9, kotel9.8ÃÄ9, kotel9.9ÃÄ9, kotel9.10ÃÄ9, kotel9.3ÃÊ9, kotel9.4ÃÊ9, kotel9.6ÃÊ9, kotel9.5ÃÊ9, kotel9.3ÃÏ9, kotel9.4ÃÏ9, kotel9.5ÃÏ9, kotel9.6ÃÏ9, kotel9.4ÃÏÇ9, kotel9.1Ø9, kotel9.2Ø9, kotel9.11Ø9, kotel9.13Ø9 |
| Network (loading) (net) | kotel9.ParNet, kotel9.Àòìîñô |
| Pipe 1->2 (pipe1_2) | kotel9.ÓÇ3, kotel9.Óç5, kotel9.Óç6, kotel9.Óç7, kotel9.Óç10 |
| Pipe 2->1 (pipe2_1) | kotel9.ÓÇ1, kotel9.ÓÇ2, kotel9.ÓÇ9, kotel9.Óç12 |
| Pipe 3->1 (pipe3_1) | kotel9.Óç8 |
| Source (pressure) (src_press) | kotel9.SrcÃÄ, kotel9.SrcÃÊ, kotel9.SrcÂîäà, kotel9.SrcÏÃ, kotel9.SrcÂîçäóõ |
| Library "Complex1 functions lib (Special.FLibComplex1)" | |
| PID regulator (pid) | kotel9_cntr.TCA1, kotel9_cntr.F_air_gas, kotel9_cntr.QAC151, kotel9_cntr.LC121, kotel9_cntr.PCA51, kotel9_cntr.FC101, kotel9_cntr.FC102, kotel9_cntr.FC103, kotel9_cntr.FC104, kotel9_cntr.FC105, kotel9_cntr.PSA76 |
| Library "Boiler Ê9" (DAQ.JavaLikeCalc.k9) | |
| Divider (Delitel) | kotel9_cntr.Air_Gas |
| Total fuel flow in boiler (Fsum) | kotel9_cntr.Fsum |
| Inversion (Inversion) | kotel9_cntr.5VP_inv |
Through the usage of the apparatus models' library and the dynamic models building conception it was obtained the dynamic model, from which you can get the parameters at any point of the schematic diagram both for the study and for testing the control algorithms.
For information about the technological process the TP parameters were created (Table 3), which provide data from selected nodes of the model.
Table 3. Technological process parameters
| Cipher | Description | Properties | Source |
| DMC Boiler9 (BlockCalc.kotel9) | |||
| LC121 | The water level in the boiler's drum | Áàðàáàí.Lo | |
| LÑA122, LSA124 | The level of water in a clean drum slot, right | %, (0;100), Precision 0 | Áàðàáàí.Lo |
| LSA123 | The level of water in a clean drum slot, left | %, (0;100), Precision 0 | Áàðàáàí.Lo |
| LCVG121 | 3FWL-9 position | %, (0;100), Precision 0 | 3ÂÏ.l_kl1 |
| LCVG122 | 3FWR-9 position | %, (0;100), Precision 0 | 3ÂÏ.l_kl2 |
| G_11SH | 11G-9 position | 11Ø9.l_kl1 | |
| G_12SH | 12G-9 position | 11Ø9.l_kl2 | |
| G_13SH | 13G-9 position | 13Ø9.l_kl1 | |
| G_14SH | 14G-9 position | 13Ø9.l_kl2 | |
| P_5VP | 5FW(1) position | 5ÂÏ.l_kl1 | |
| P_5VP_2 | 5FW(2) position | 5ÂÏ.l_kl2 | |
| P_7VP | 7FW position | 7ÂÏ.l_kl1 | |
| P_4GP9 | 4GN9 position | 4ÃÏ9.l_kl1 | |
| P_5GP9 | 5GN9 position | 5ÃÏ9.l_kl1 | |
| P_7GD | 7GBF position | 7ÃÄ9.l_kl1 | |
| P_8GD | 8GBF position | 8ÃÄ9.l_kl1 | |
| FCVG102 | 5GN-9 position | 5ÃÏ9.l_kl1 | |
| FCVG103 | 7GBF9 position | 7ÃÄ9.l_kl1 | |
| FCVG104 | 8GN-9 position | 8ÃÄ9.l_kl1 | |
| FCVG105 | 4GC-9 position | 4ÃÊ9.l_kl1 | |
| TCVG1_1 | 7FW-9 position | 7ÂÏ9.l_kl1 | |
| TCVG1_2 | 5FWL-9 position | 5ÂÏ9.l_kl1 | |
| PCVG76 | SEA productivity | rpm, (0;100), Precision 1 | ÄÑÀ.N |
| PCVG77 | SEB productivity | rpm, (0;100), Precision 1 | ÄÑÁ.N |
| FCV106 | BFA productivity | rpm, (0;100), Precision 1 | ÄÂÀ.N |
| FCV107 | BFB productivity | rpm, (0;100), Precision 1 | ÄÂÁ.N |
| PCA51 | Steam pressure after the MSV | at, (0;50), Precision 2 | 4ÃÏÇ9.Po |
| PSA52 | Steam pressure in the the boiler's drum | at, (0;40), Precision 2 | Áàðàáàí.Po1 |
| PCA52 | Steam pressure in the boiler's drum | at, (0;50), Precision 2 | Áàðàáàí.Po1 |
| PSA52_1 | Steam pressure in the boiler's drum | at, (0;40), Precision 2 | Áàðàáàí.Po1 |
| PSA53 | GN pressure before the regulating valve | at, (0;40), Precision 2 | 3ÃÏ9.Po |
| PSA53_1 | GN pressure before the diaphragm | at, (0;40), Precision 2 | 3ÃÏ9.Po |
| PSA53_2 | GN pressure before the diaphragm | at, (0;40), Precision 2 | 3ÃÏ9.Po |
| PSA54 | GN pressure after the regulating valve | at, (0;1.5), Precision 3 | 5ÃÏ9.Po |
| PA55 | GN pressure before the left burner | at, (0;40), Precision 2 | 6ÃÏ9.Po |
| PA56 | GN pressure before the right burner | at, (0;40), Precision 2 | 6ÃÏ9.Po |
| PSA57_1, PSA57_2 | GBF pressure on the general pipeline. | at, (0;2), Precision 2 | ÓÇ3.Pi |
| PSA59 | GBF pressure after valve on the left gas pipeline | at, (1;2), Precision 3 | 10ÃÄ9.Po |
| PSA60 | GBF pressure after valve on the right gas pipeline | at, (1;2), Precision 3 | 9ÃÄ9.Po |
| P61 | GBF pressure before the left burner | at, (0;1.6), Precision 2 | 9ÃÄ9.Po |
| P62 | GBF pressure before the right burner | at, (0;1.6), Precision 2 | 10ÃÄ9.Po |
| PSA63_1 | GC pressure after 5GC-9 | at, (0;2), Precision 2 | 5ÃÊ9.Po |
| PSA63_2 | GC pressure after 3GC-9 | at, (0;2), Precision 2 | 3ÃÊ9.Po |
| PSA64 | GC pressure after the regulating valve | at, (0;2), Precision 3 | 4ÃÊ9.Po |
| P65 | GC pressure before the left burner | at, (0;1.6), Precision 2 | 6ÃÊ9.Po |
| P66 | GC pressure before the right burner | at, (0;1.6), Precision 2 | 6ÃÊ9.Po |
| P67 | The air pressure before the first stage of A/H to the left. | at, (0;1.2), Precision 2 | ÓÇ9.Po |
| P72 | The air pressure in the upper tier of the left burner | at, (0;1.2), Precision 2 | ÓÇ2.Po |
| P68 | The air pressure before the first stage of A/H to the right. | at, (0;1.2), Precision 2 | ÓÇ9.Po |
| PSA70 | Air pressure after the second stage of air-heater | at, (0;1.2), Precision 2 | ÂÏ2.Po2 |
| PSA71 | Air pressure after the second stage of air-heater | at, (0;1.2), Precision 2 | ÂÏ2.Po2 |
| P73, PSA73 | The air pressure in the upper tier of the right burner | at, (0;1.16), Precision 2 | ÓÇ2.Po |
| P74 | The air pressure on the lower tier of the left burner | at, (0;1.16), Precision 2 | ÓÇ2.Po |
| P75, PSA75 | The air pressure on the lower tier of the right burner | at, (0;1.16), Precision 2 | ÓÇ2.Po |
| PCSA76 | The vacuum in the fire chamber on the left | at, (0.9;1), Precision 3 | Òîïêà.Po |
| PCSA77 | The vacuum in the fire chamber on the right | at, (0.9;1), Precision 3 | Òîïêà.Po |
| P78 | The vacuum in front of "SE-A" | at, (0.9;1), Precision 2 | 1Ø9.Po |
| P79 | The vacuum in front of "SE-B" | at, (0.9;1), Precision 2 | 2Ø9.Po |
| PSA80 | FW pressure on the left feeding line | at, (0;60), Precision 2 | SrcÂîäà.Po |
| PSA81 | FW pressure on the right feeding line | at, (0;60), Precision 2 | SrcÂîäà.Po |
| PSA85 | Air pressure after the air heater | at, (0;2), Precision 3 | ÂÏ2.Po2 |
| P103 | GBF pressure on the diaphragm on the left | at, (0;2), Precision 2 | ÓÇ3.Po2 |
| P104 | GBF pressure on the diaphragm on the right | at, (0;2), Precision 2 | ÓÇ3.Po1 |
| Src_GP_Pi | The inlet pressure at the source of GN | SrcÏÃ.Pi | |
| P_GP_S | GN pressure after the source | SrcÏÃ.Po | |
| P_GP_4GP | GN pressure after 4GN9 | 4ÃÏ9.Po | |
| P_3VP_1 | 3FW9(1) position | 3ÂÏ.l_kl1 | |
| P_3GP9 | 3GN9 position | 3ÃÏ9.l_kl1 | |
| P_6GP9_1 | 6GN9_1 position | 6ÃÏ9.l_kl1 | |
| P_6GP9_2 | 6GN9_2 position | 6ÃÏ9.l_kl2 | |
| P_5GK | 5GC position | 5ÃÊ9.l_kl1 | |
| Pbar | The pressure in the boiler's drum | Áàðàáàí.Po1 | |
| TCA1 | Steam temperature after MSV | 4ÃÏÇ9.To | |
| F_3VP | Water flow after 3FW | 3ÂÏ.Fo | |
| F_5VP | Water flow after 5FW | 5ÂÏ.Fo | |
| F_7VP | Water flow after 7FW | 7ÂÏ.Fo | |
| Fbar | Water flow into the drum | Áàðàáàí.Fi1 | |
| F_UZ8 | Water flow after UZ8 | Óç8.Fo | |
| FC101 | Steam flow from boiler | t/h, (0;100), Precision 2 | 4ÃÏÇ9.Fo |
| FC102 | Flow of the natural gas after 3GN9 | 3ÃÏ9.Fo | |
| FC102_0 | Natural gas flow after it source | SrcÏÃ.Fo | |
| FC102_1 | Natural gas flow after 4GN9 | 4ÃÏ9.Fo | |
| FC102_2 | Natural gas flow after 5GN9 | 5ÃÏ9.Fo | |
| FC102_3 | Natural gas flow after 6GN9 | 6ÃÏ9.Fo | |
| FC103 | GBF flow on the left gas pipeline | 5ÃÄ9.Fi | |
| FC104 | GBF flow on the right gas pipeline | 6ÃÄ9.Fi | |
| FC105 | Flow of coke gas after 5GC9 | 5ÃÊ9.Fo | |
| FC106 | Air flow to the left burner | t/h, (0;100), Precision 1 | ÓÇ2.Fi1 |
| FC107 | Air flow to the right burner | t/h, (0;100), Precision 1 | ÓÇ2.Fi2 |
| FA108 | The flow of air-superheater on the right feeding line | t/h, (0;200), Precision 2 | SrcÂîäà.Fo |
| F109 | Water flow for the thermostat | t/h, (0;200), Precision 2 | 7ÂÏ.Fo |
| FA110 | The flow of air-superheater on the left feeding line | t/h, (0;200), Precision 2 | SrcÂîäà.Fo |
| QA151 | The oxygen content in FG after the superheater | %, (0;20), Precision 2 | Òîïêà.O2 |
| QA152 | The CO content in FG after the superheater | %, (0;20), Precision 2 | Òîïêà.CO |
| QA153 | Oxygen content in the exhaust FG | %, (0;20), Precision 2 | Òîïêà.O2 |
| T2 | Natural gas temperature | deg.K, (223;323), Precision 2 | 3ÃÏ9.To |
| T3 | GBF temperature | deg.K, (273;373), Precision 2 | 5ÃÄ9.Ti |
| T5 | The temperature of the GC before boiler | deg.K, (273;373), Precision 2 | 4ÃÊ9.To |
| T7 | Air temperature after the second stage of air-heater on the left | deg.K, (273;773), Precision 2 | ÂÏ2.To2 |
| T8 | Air temperature after the second stage of air-heater on the right | deg.K, (273;773), Precision 2 | ÂÏ2.To2 |
| T13 | FG temperature before superheater on the left | deg.K, (273;1027), Precision 2 | Áàðàáàí.To2 |
| T14 | FG temperature before superheater on the right | deg.K, (273;1027), Precision 2 | Áàðàáàí.To2 |
| T15 | FG temperature before 2 stage of economizer on the left | deg.K, (273;873), Precision 2 | ÏÏ.To1 |
| T16 | FG temperature before 2 stage of economizer on the right | deg.K, (273;873), Precision 2 | ÏÏ.To1 |
| T17 | FG temperature after 2 stage of economizer on the left | deg.K, (273;873), Precision 2 | ÝÊ2.To1 |
| T18 | FG temperature after 2 stage of economizer on the right | deg.K, (273;873), Precision 2 | ÝÊ2.To1 |
| T19 | FG temperature before the first stage of air-heater on the left | deg.K, (273;873), Precision 2 | ÝÊ1.To1 |
| T20 | FG temperature before the first stage of air-heater on the right | deg.K, (273;873), Precision 2 | ÝÊ1.To1 |
| T21 | FG temperature before the second stage of air-heater on the left | deg.K, (273;873), Precision 2 | ÝÊ2.To1 |
| T22 | FG temperature before the second stage of air-heater on the right | deg.K, (273;873), Precision 2 | ÝÊ2.To1 |
| T23 | FG temperature before 1 stage of economizer on the left | deg.K, (273;873), Precision 2 | ÂÏ2.To1 |
| T24 | FG temperature before 1 stage of economizer on the right | deg.K, (273;873), Precision 2 | ÂÏ2.To1 |
| TA25 | FG temperature before th "SE-A" | deg.K, (273;673), Precision 2 | 1Ø9.To |
| TA26 | FG temperature before th "SE-B" | deg.K, (273;673), Precision 2 | 2Ø9.To |
| T35 | The temperature of water on the left feeding line | deg.K, (273;473), Precision 2 | 3ÂÏ.To |
| T36 | The temperature of water on the right feeding line | deg.K, (273;473), Precision 2 | 3ÂÏ.To |
| T37 | The water temperature after the economizer on the left | deg.K, (273;673), Precision 2 | ÝÊ2.To2 |
| T38 | The water temperature after the economizer on the right | deg.K, (273;673), Precision 2 | ÝÊ2.To2 |
| DMC Boiler9 Controller (BlockCalc.kotel9_cntr) | |||
| TCA1 | Steam temperature at the outlet | K, (273;800), Precision 0 | TCA1.* |
| QAC151 | The percentage of oxygen in the flue gases. | %, (0;15), Precision 1 | QAC151.* |
| LC121 | Level in the boiler's drum | %, (0;100), Precision 1 | LC121.* |
| 5VP | %, (0;100), Precision 1 | 5VP_inv.OVar | |
| FC101 | Steam flow from the boiler | t/h, (0;150), Precision 0 | FC101.* |
| FC102 | Natural gas flow | t/h, (0;6), Precision 1 | FC102.* |
| FC103 | Flow of blast furnace gas on the left gas pipeline | t/h, (0;70), Precision 1 | FC103.* |
| FC104 | Flow of blast furnace gas on the right gas pipeline | t/h, (0;70), Precision 1 | FC104.* |
| FC105 | Flow of the coke oven gas | t/h, (0;10), Precision 1 | FC105.* |
| PSA76 | The vacuum in the fire chamber | at, (0.9;1), Precision 3 | PSA76.* |
2.3 Regulation
The dynamic model itself may be unstable without control. For example, the drum level parameter does not have the self-regulation and goes to extremes in the case of the balance absence in the control parameters. Because of this reason, as well as to create the self-sustaining model, that can operate autonomously and without the PLC as a controller, the regulators controller's object was created for the boiler's model according to the regulation schemes in Fig. 2 - 4.
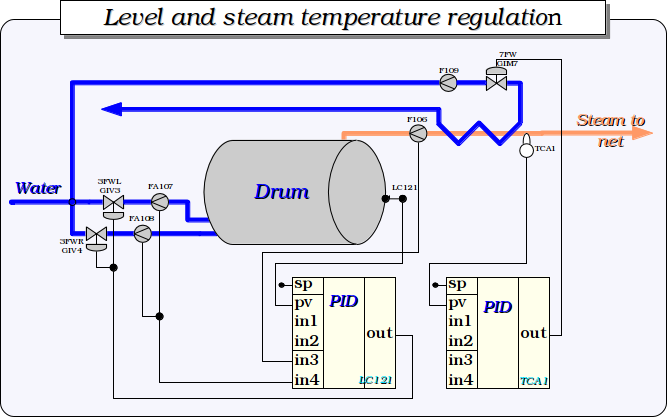
Fig. 2. Level and steam temperature regulation.
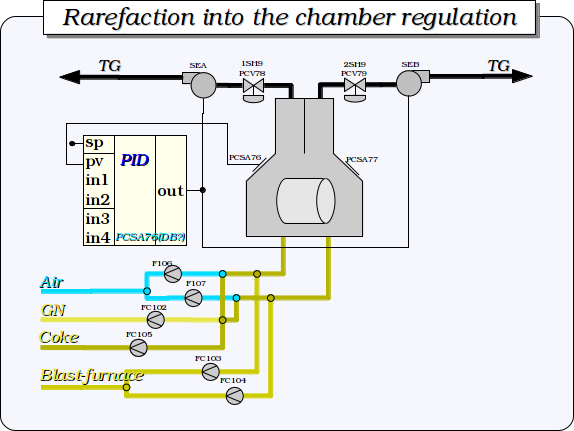
Fig. 3. Rarefaction in the furnance regulation.
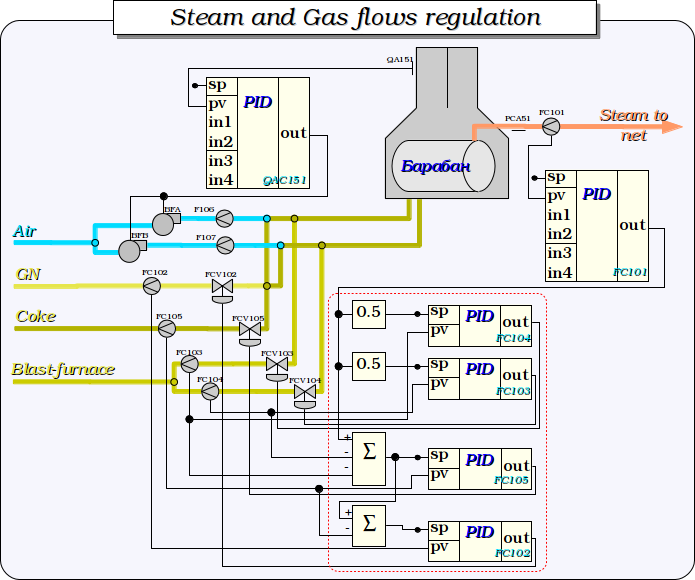
Fig. 4. Steam and Gas flows regulation.
3 User interface
The model's user interface contains eleven signal objects (Fig. 5). Each object contains several mnemo, graphics group, contour group and overviews group.
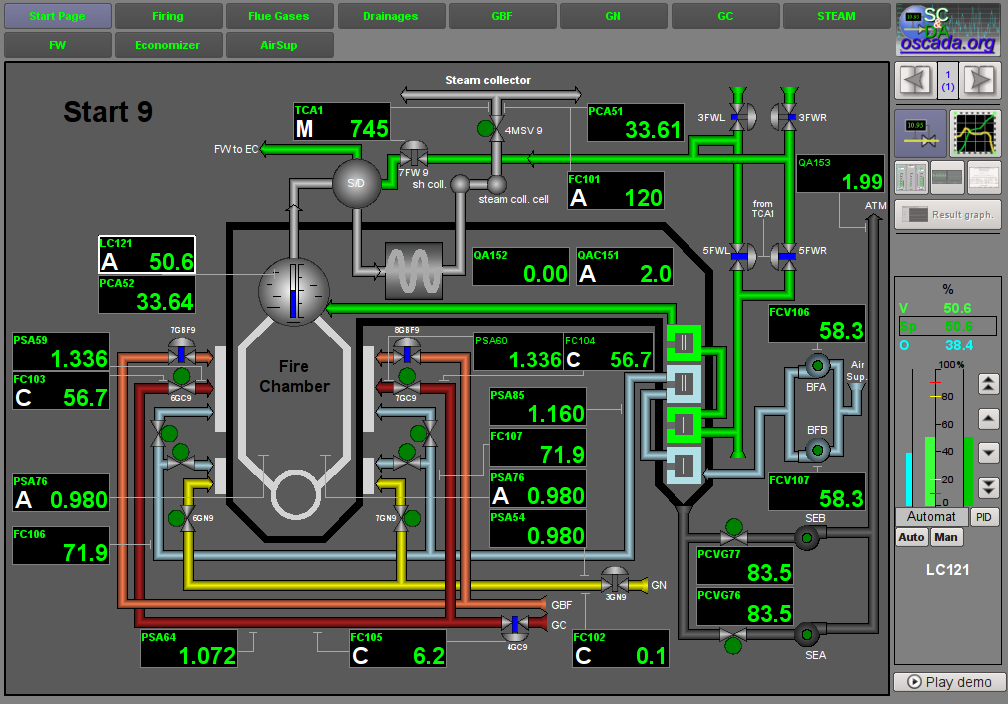
Fig. 5. General view of the user interface window.
3.1 Signal object "Start"
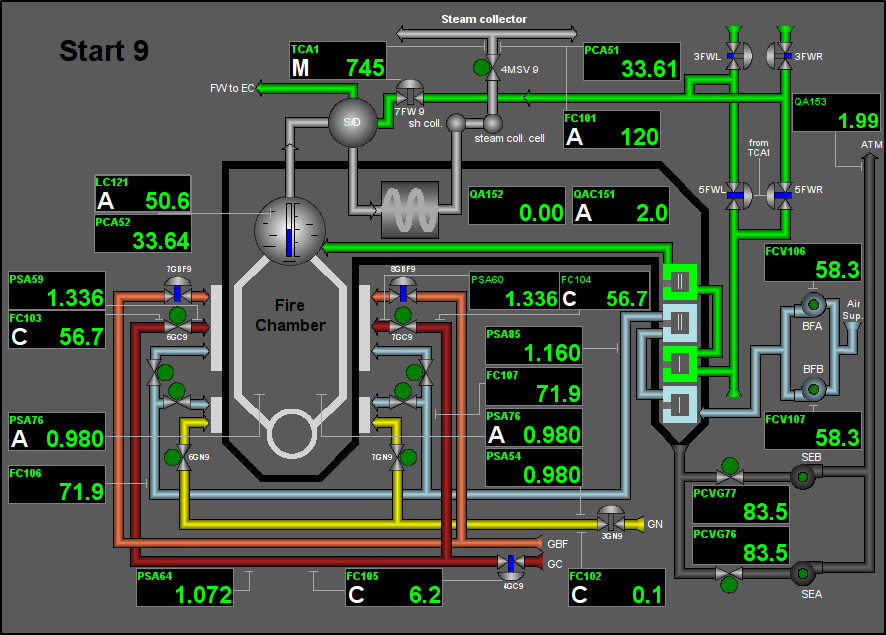
Fig. 6. Signal object "Start" mnemo.
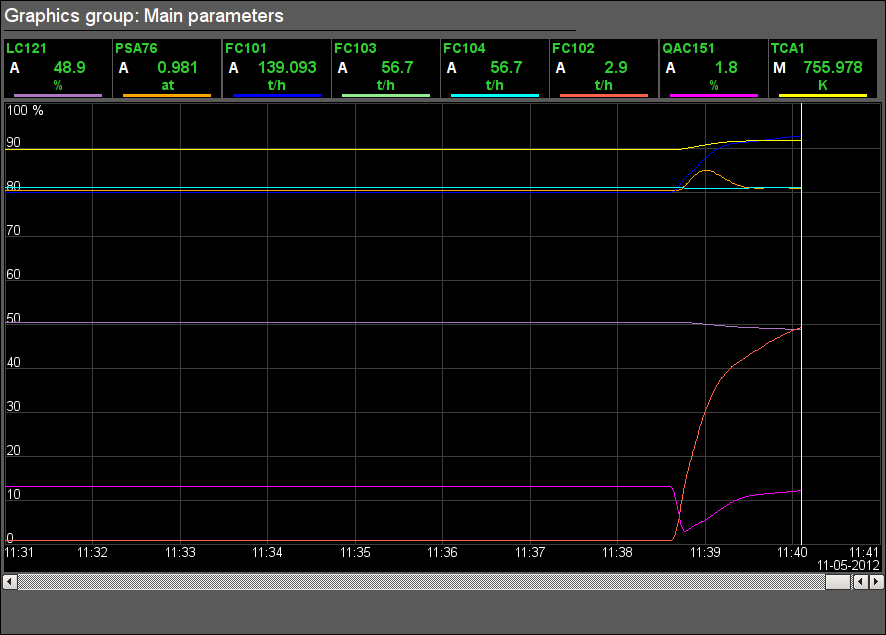
Fig. 7. Signal object "Start" graphics group.
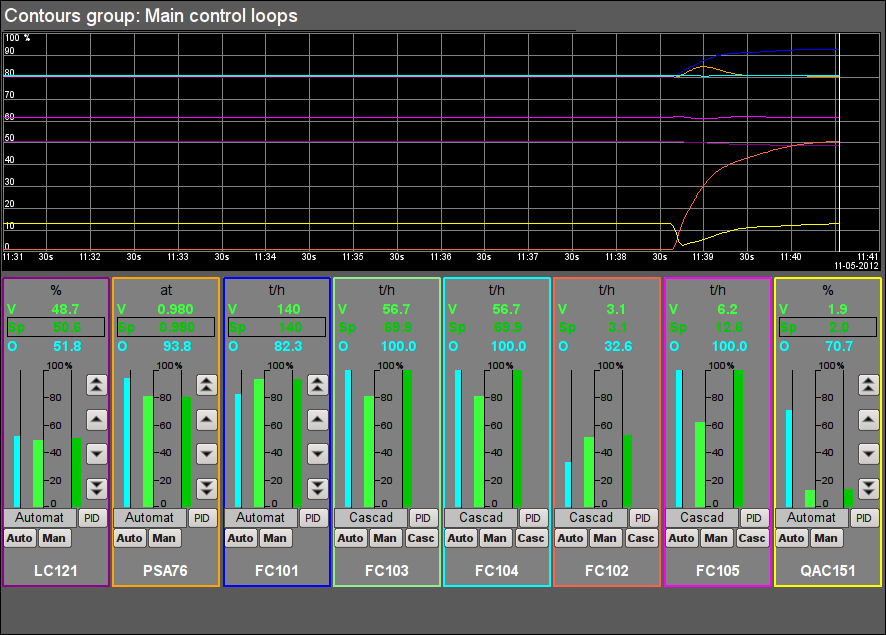
Fig. 8. Signal object "Start" contours group.
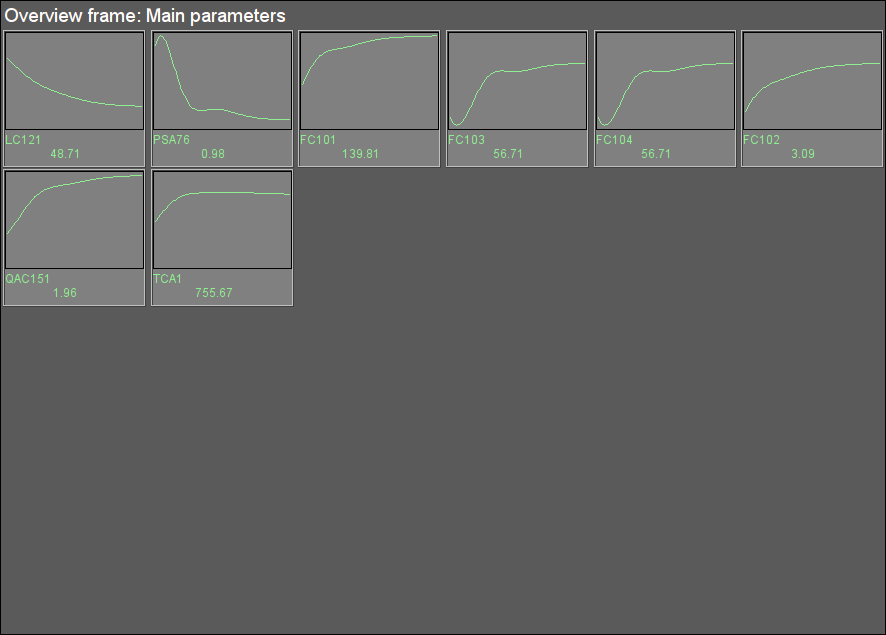
Fig. 9. Signal object "Start" overview group.
3.2 Signal object "Firing"
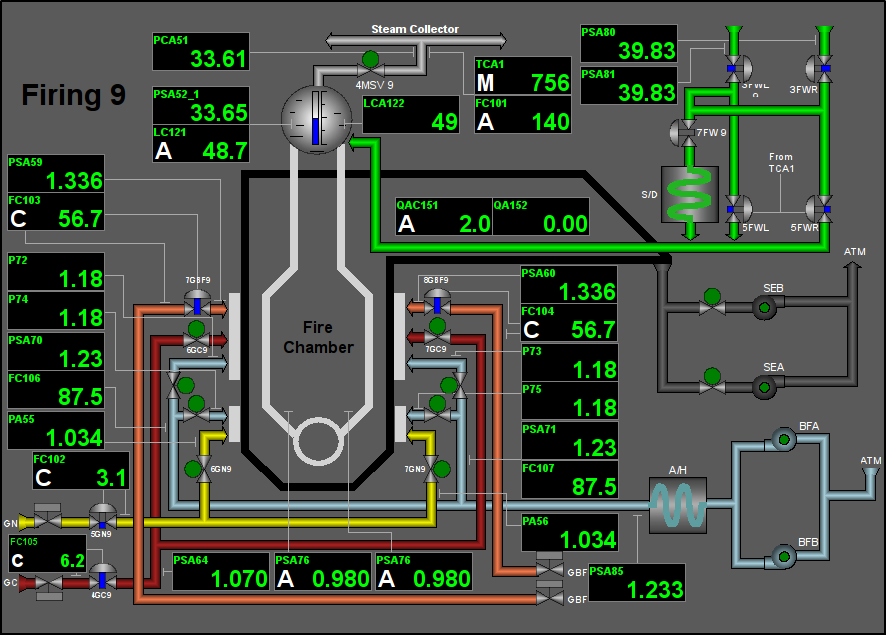
Fig. 10. Signal object "Firing" mnemo.
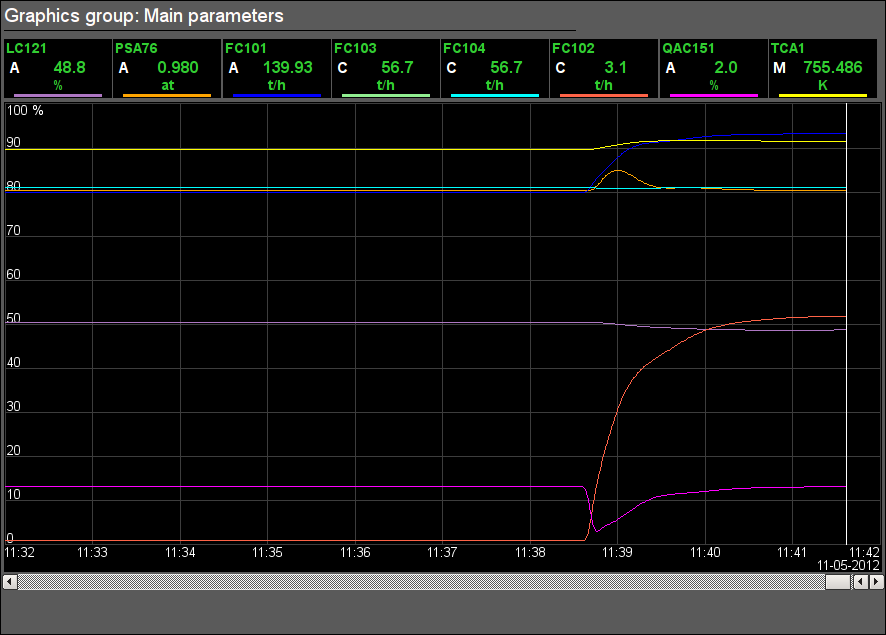
Fig. 11. Signal object "Firing" graphics group.
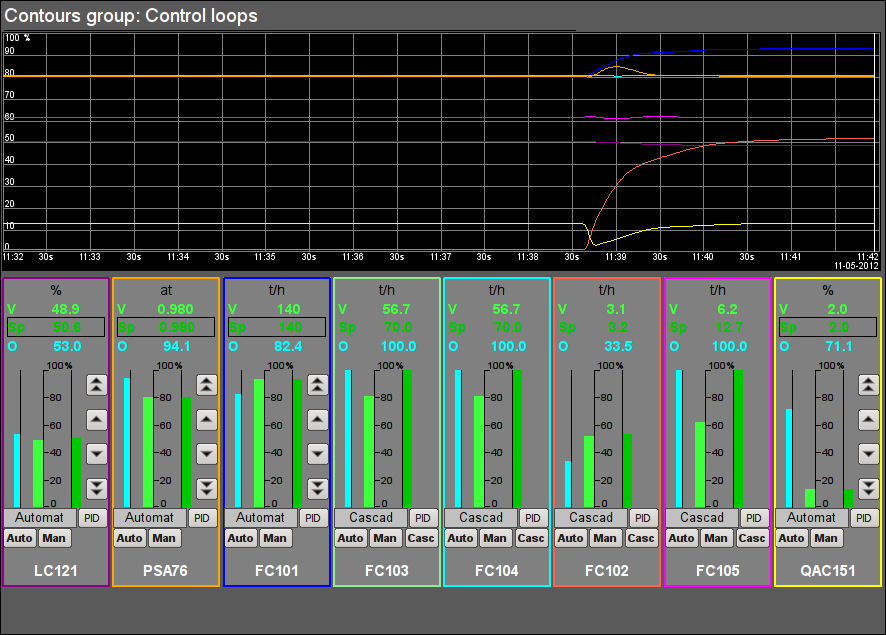
Fig. 12. Signal object "Firing" contour group.
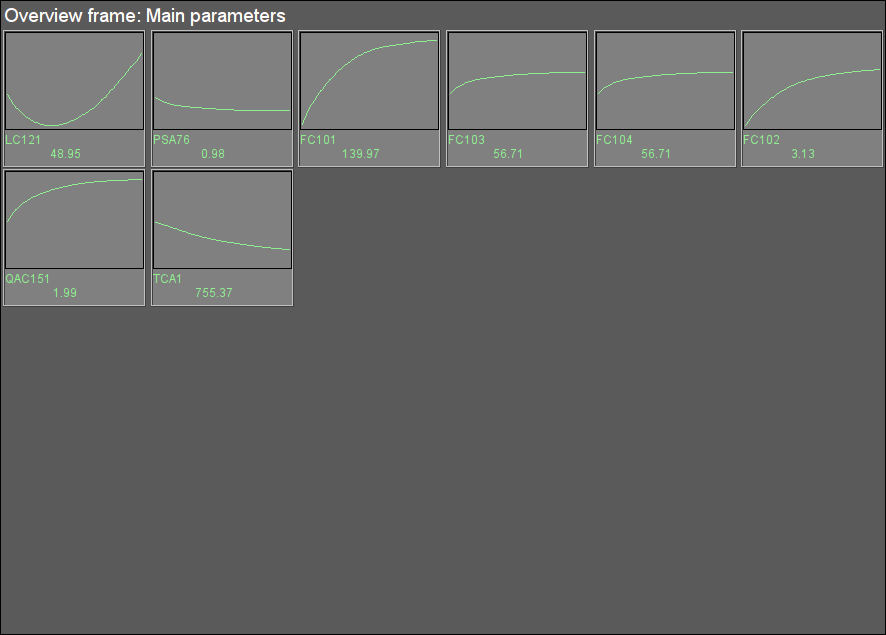
Fig. 13. Signal object "Firing" overview group.
3.3 Signal object "Flue Gases"
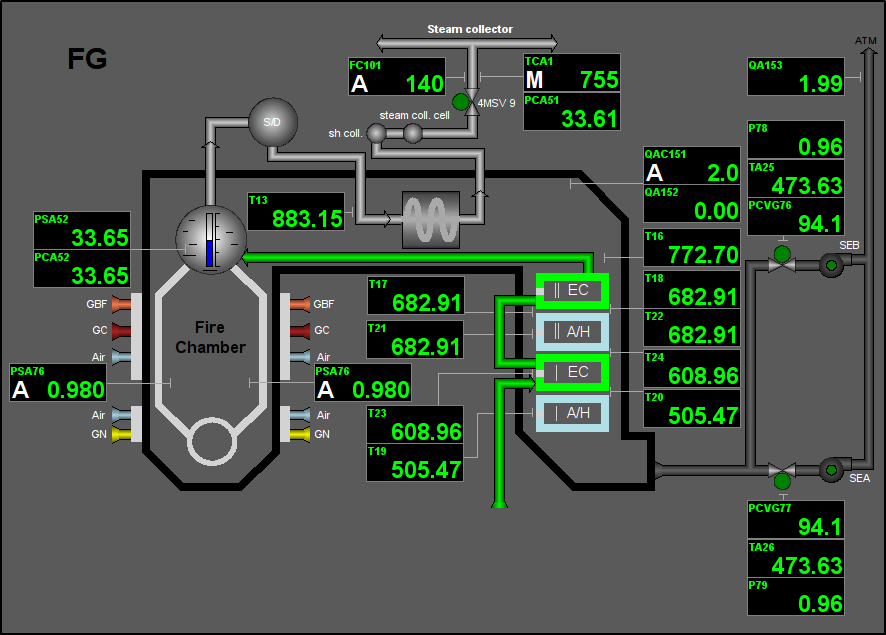
Fig. 14. Signal object "Flue Gases" mnemo.
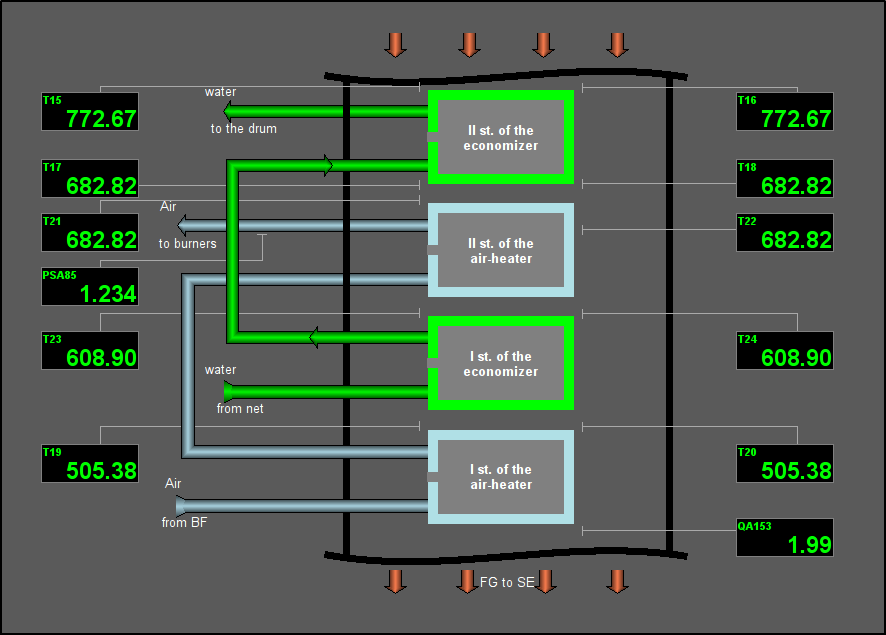
Fig. 15. Signal object "Flue Gases" mnemo 2.
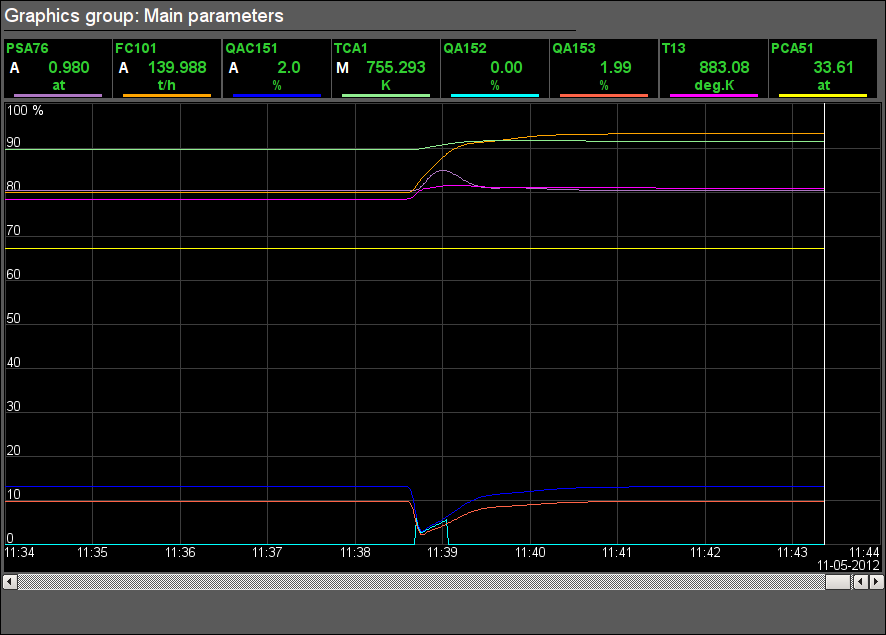
Fig. 16. Signal object "Flue Gases" graphics group.
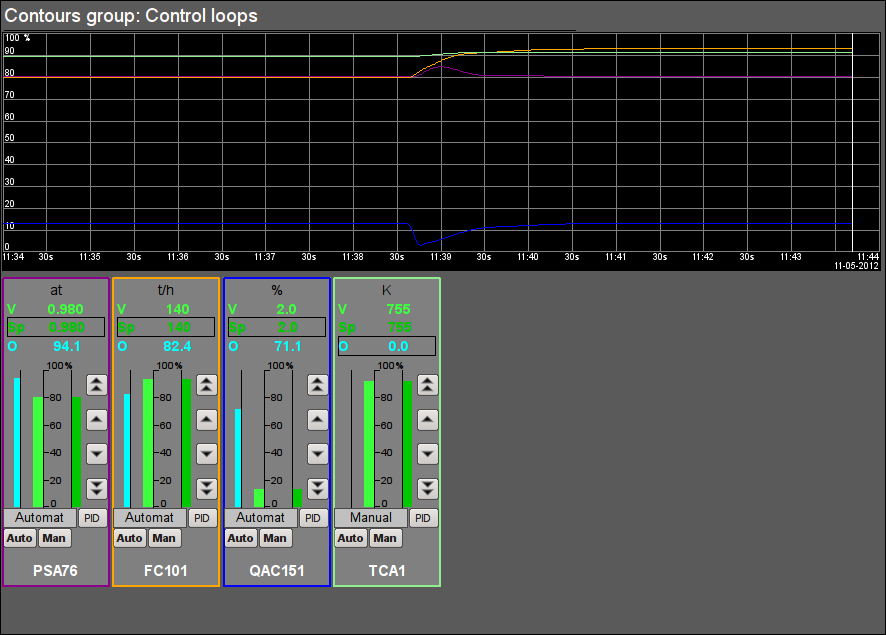
Fig. 17. Signal object "Flue Gases" contour group.
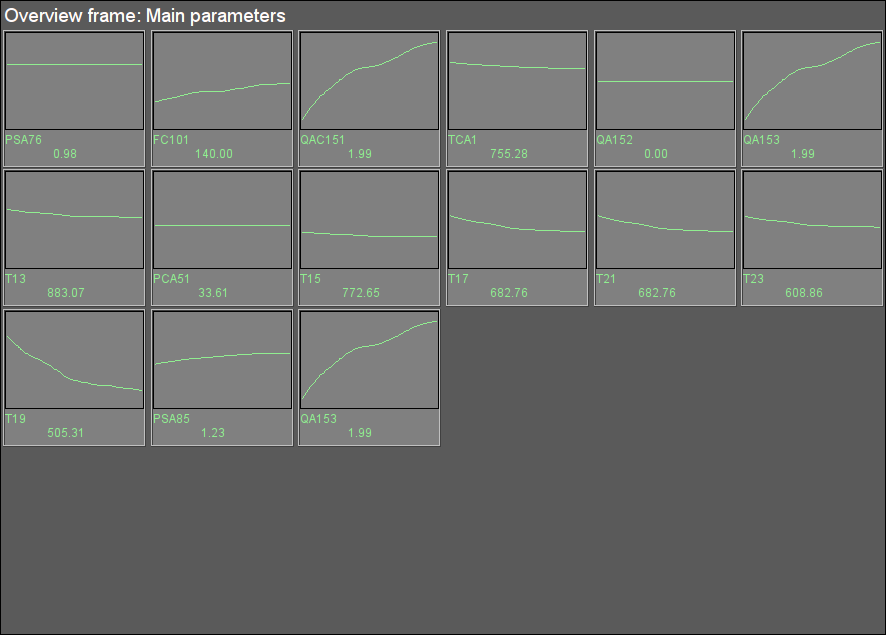
Fig. 18. Signal object "Flue Gases" overview group.
3.4 Signal object "Drainages"
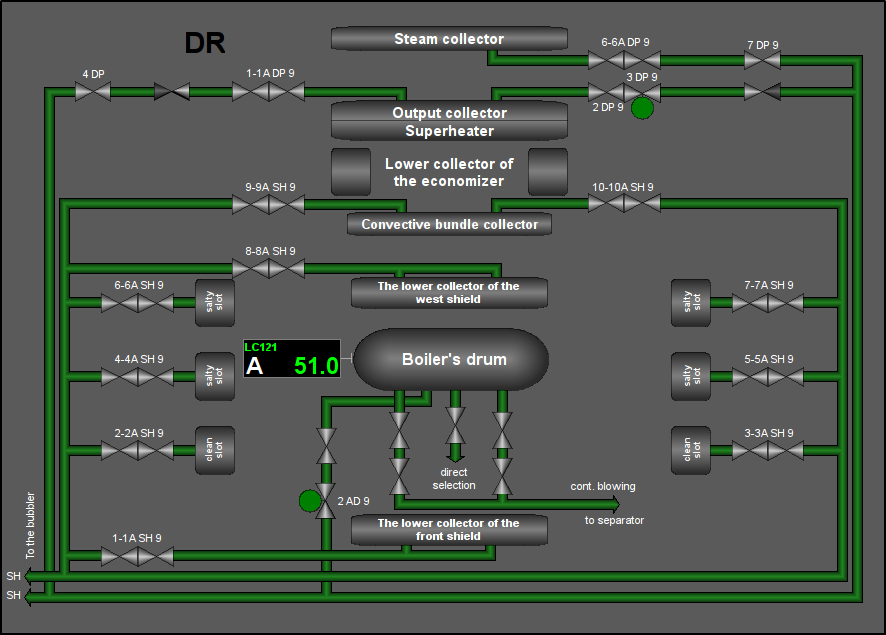
Fig. 19. Signal object "Drainages" mnemo.
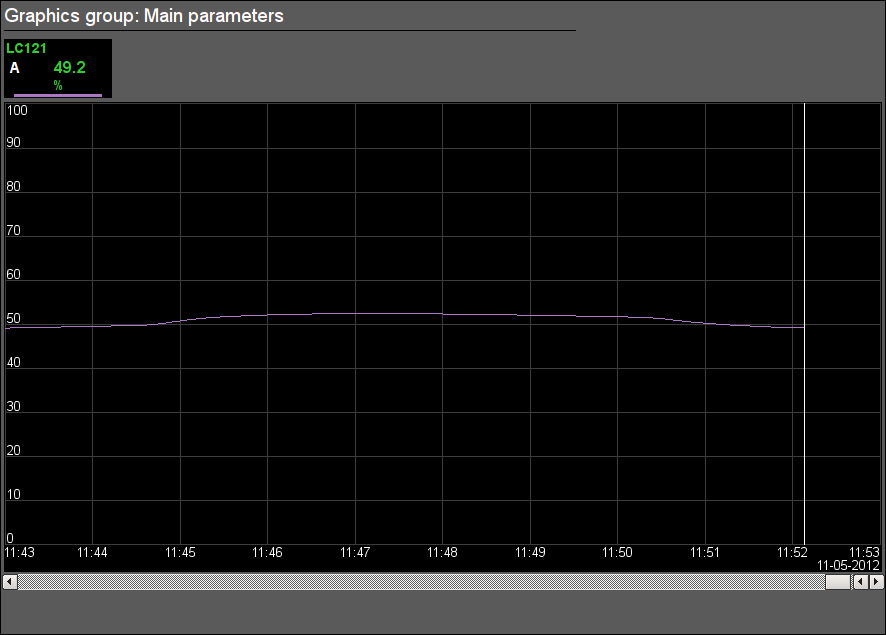
Fig. 20. Signal object "Drainages" graphics group.
Fig. 21. Signal object "Drainages" contour group.
Fig. 22. Signal object "Drainages" overview group.
3.5 Signal object "GBF"
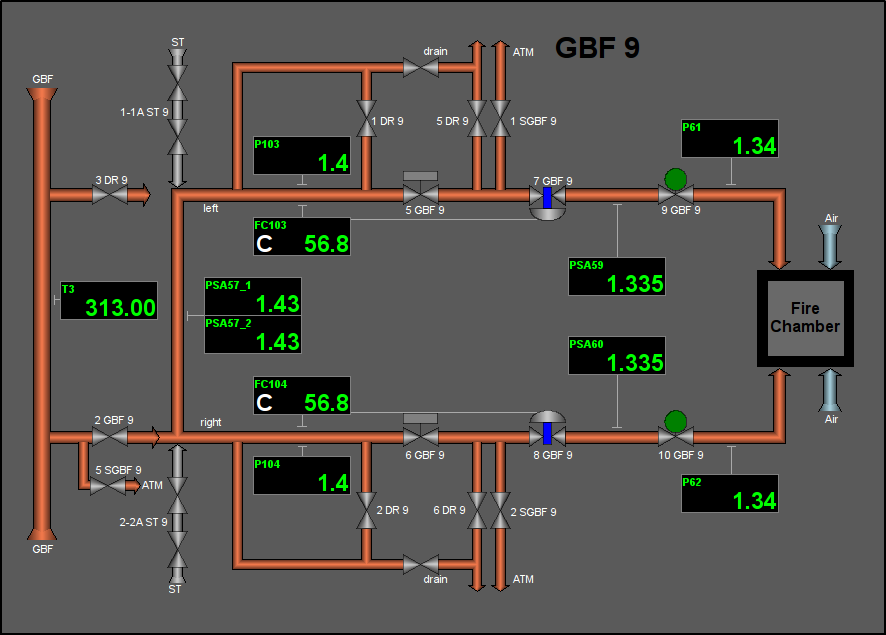
Fig. 23. Signal object "GBF" mnemo.
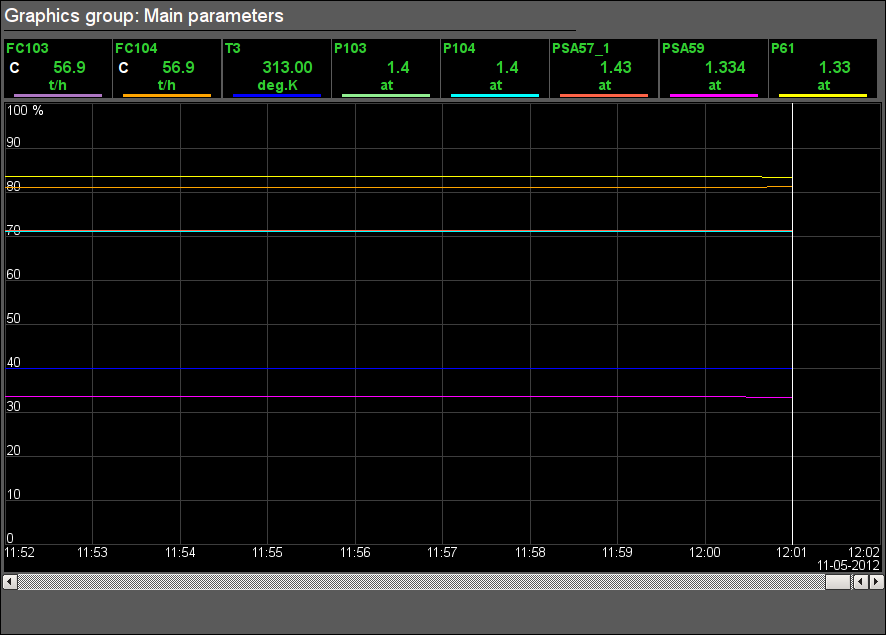
Fig. 24. Signal object "GBF" graphics group.
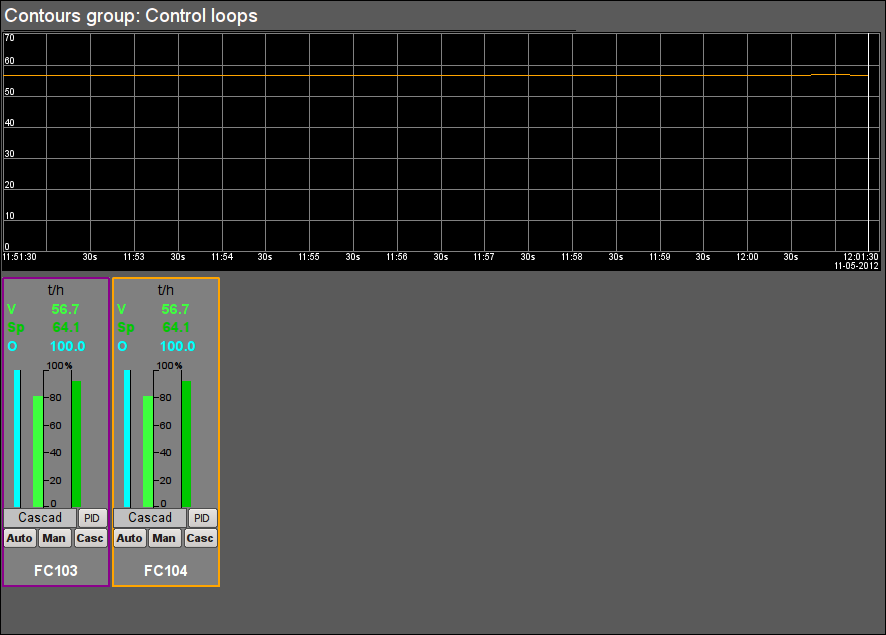
Fig. 25. Signal object "GBF" contour group.
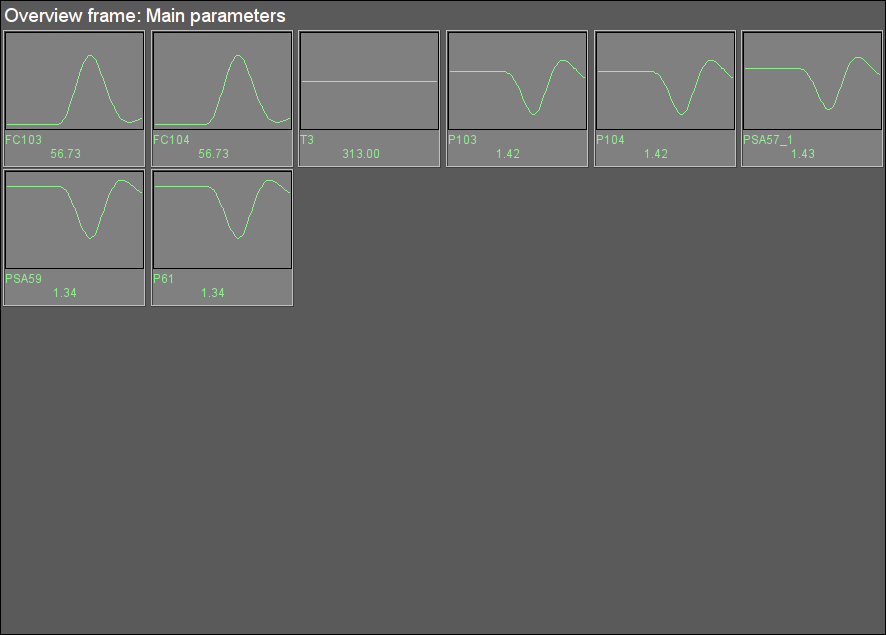
Fig. 26. Signal object "GBF" overview group.
3.6 Signal object "GN"
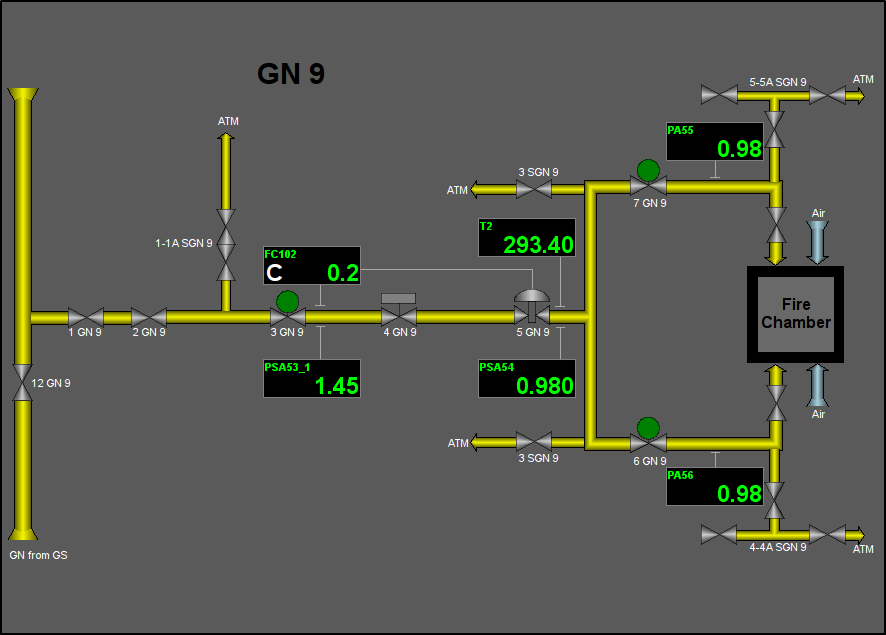
Fig. 27. Signal object "GN" mnemo.
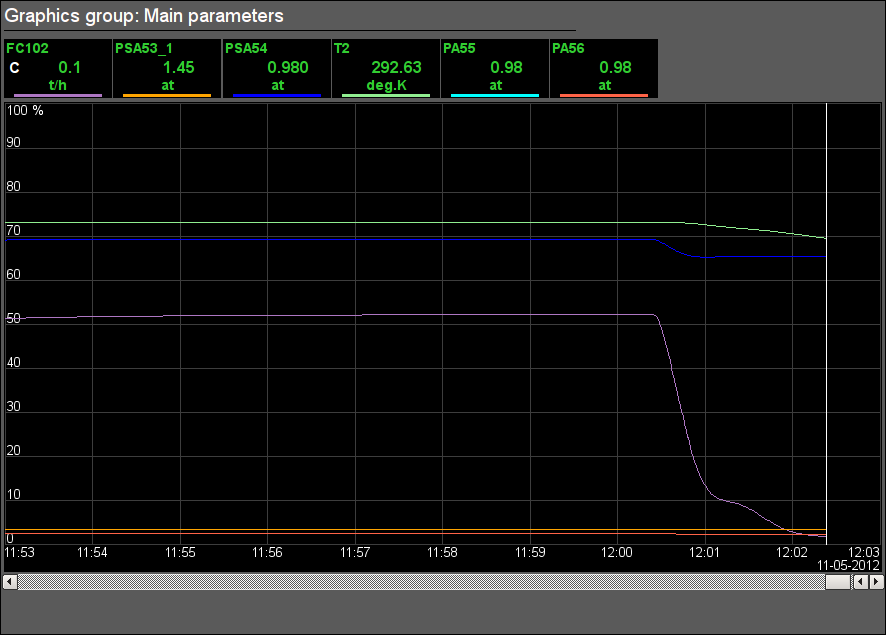
Fig. 28. Signal object "GN" graphics group.
Fig. 29. Signal object "GN" contour group.
Fig. 30. Signal object "GN" overview group.
3.7 Signal object "GC"
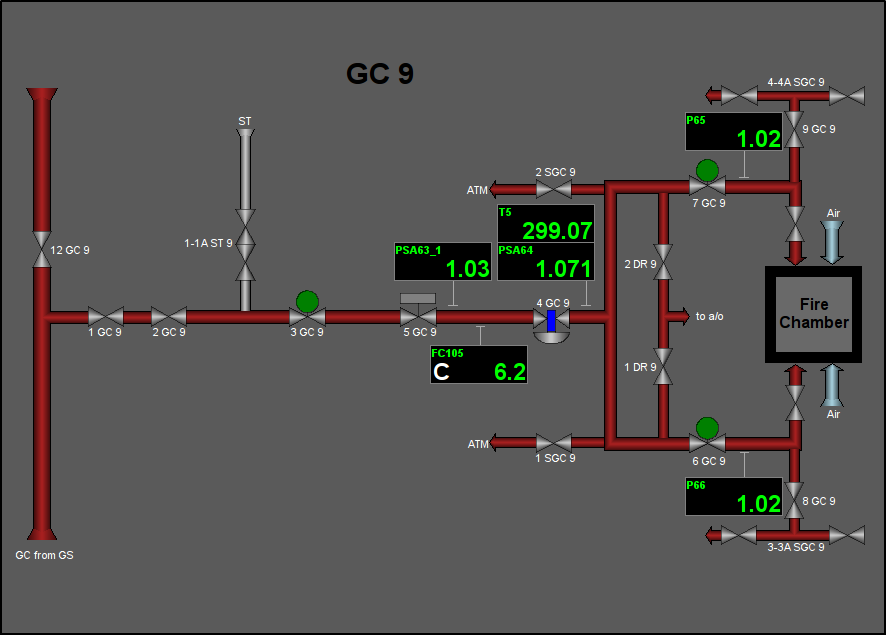
Fig. 31. Signal object "GC" mnemo.
Fig. 32. Signal object "GC" graphics group.
Fig. 33. Signal object "GC" contour group.
Fig. 34. Signal object "GC" overview group.
3.8 Signal object "STEAM"
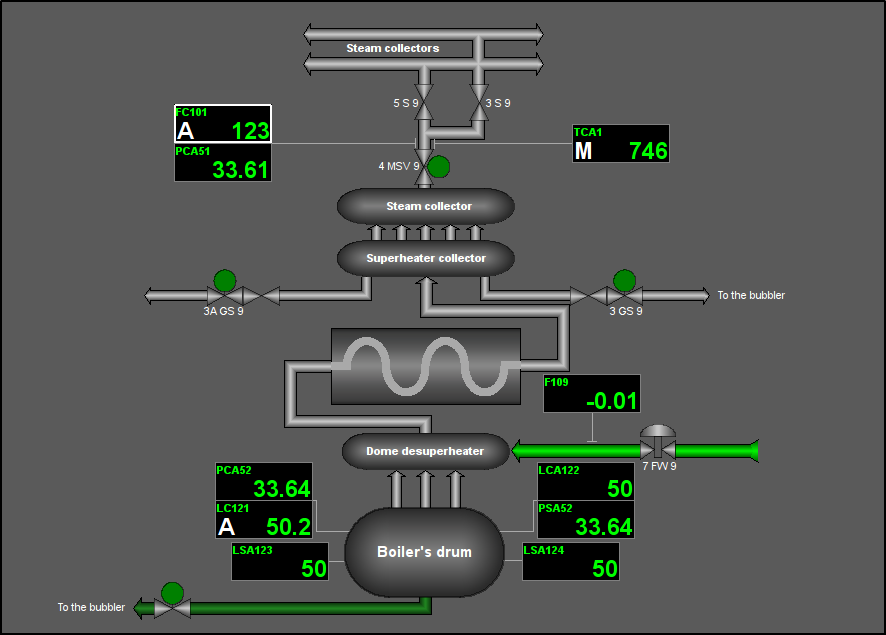
Fig. 35. Signal object "STEAM" mnemo.
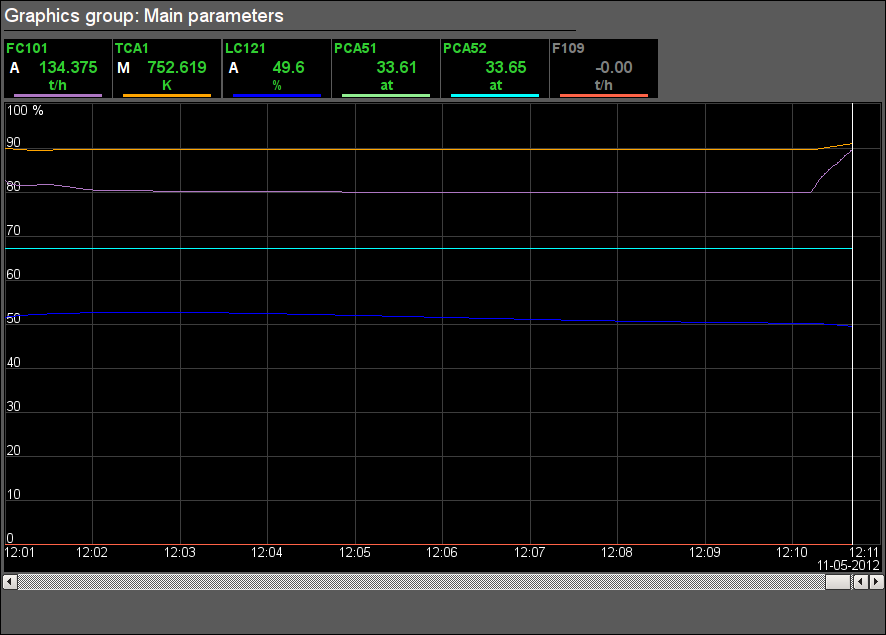
Fig. 36. Signal object "STEAM" graphics group.
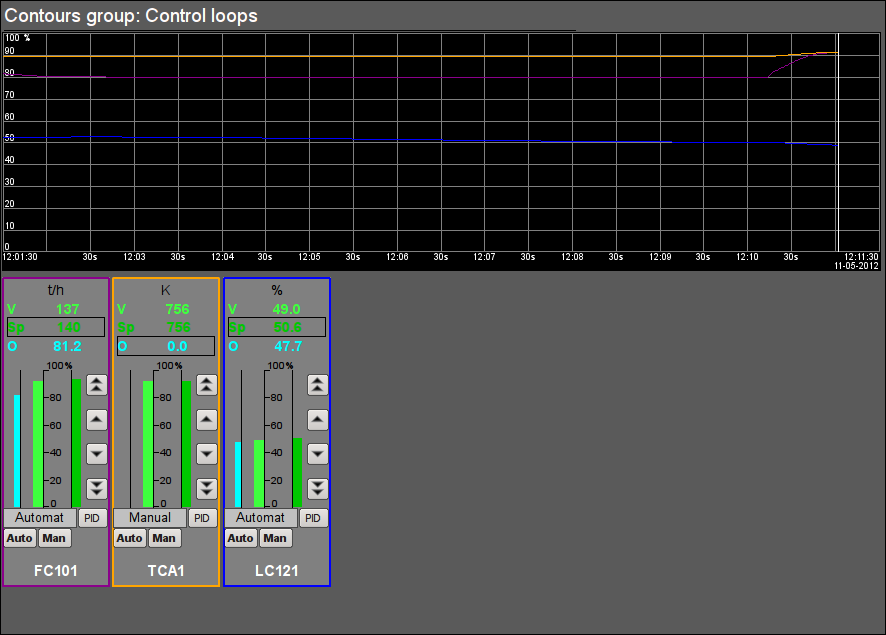
Fig. 37. Signal object "STEAM" contour group.
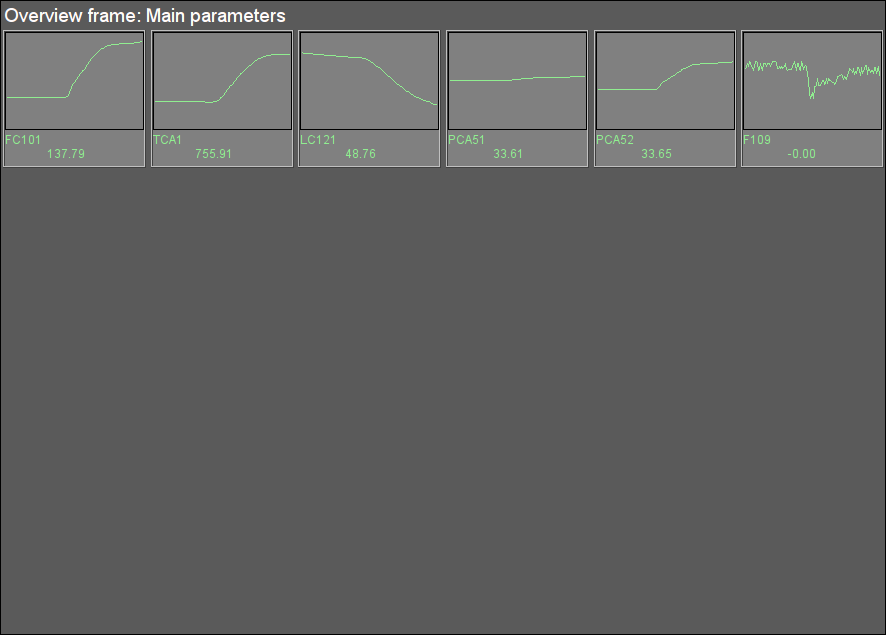
Fig. 38. Signal object "STEAM" overview group.
3.9 Signal object "FW"
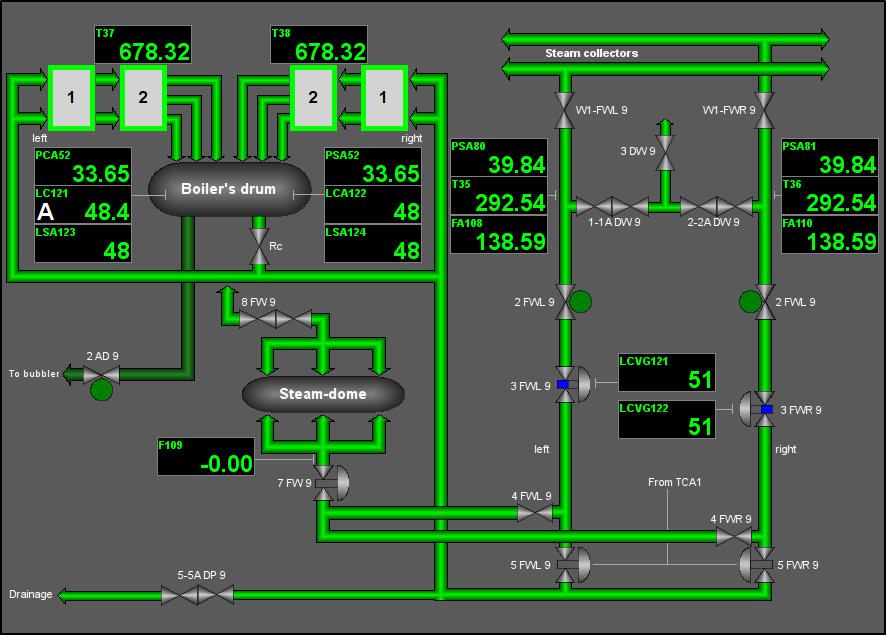
Fig. 39. Signal object "FW" mnemo.
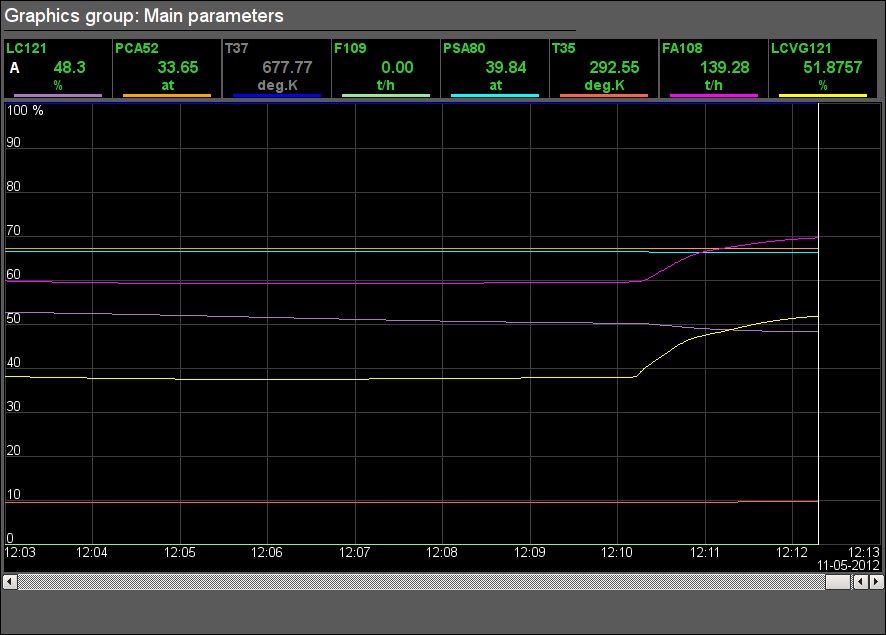
Fig. 40. Signal object "FW" graphics group.
Fig. 41. Signal object "FW" contour group.
Fig. 42. Signal object "FW" overview group.
3.10 Signal object "Economizer"
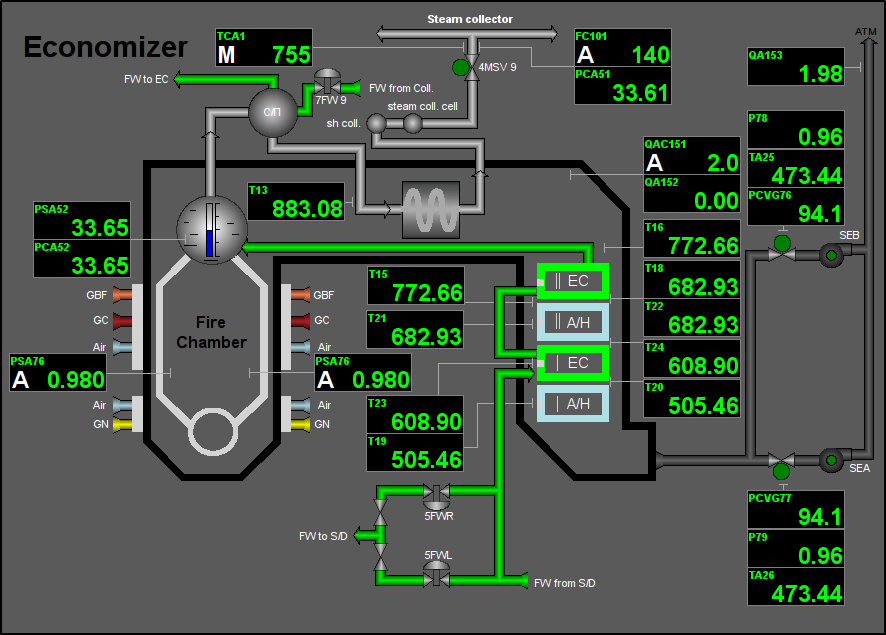
Fig. 43. Signal object "Economizer" mnemo.
Fig. 44. Signal object "Economizer" graphics group.
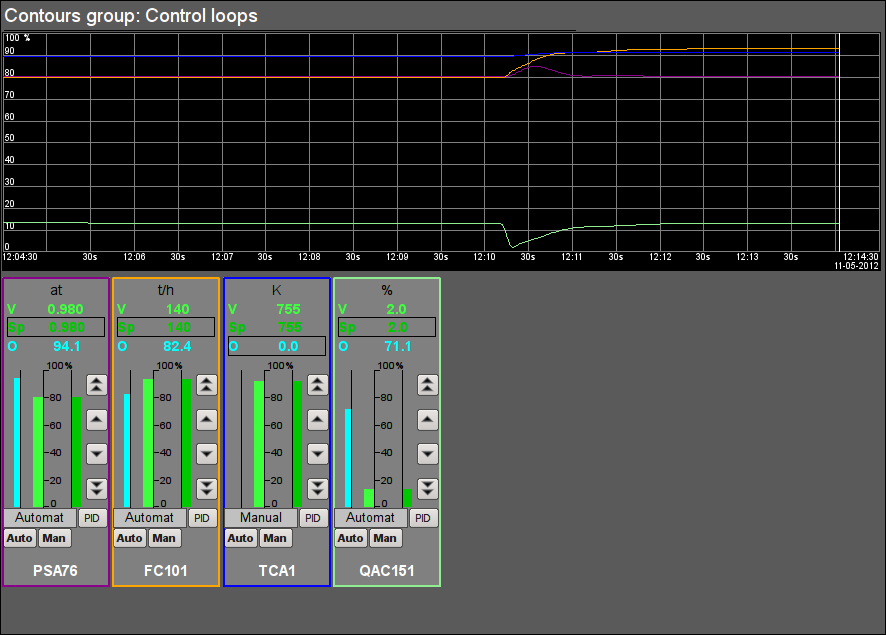
Fig. 45. Signal object "Economizer" contour group.
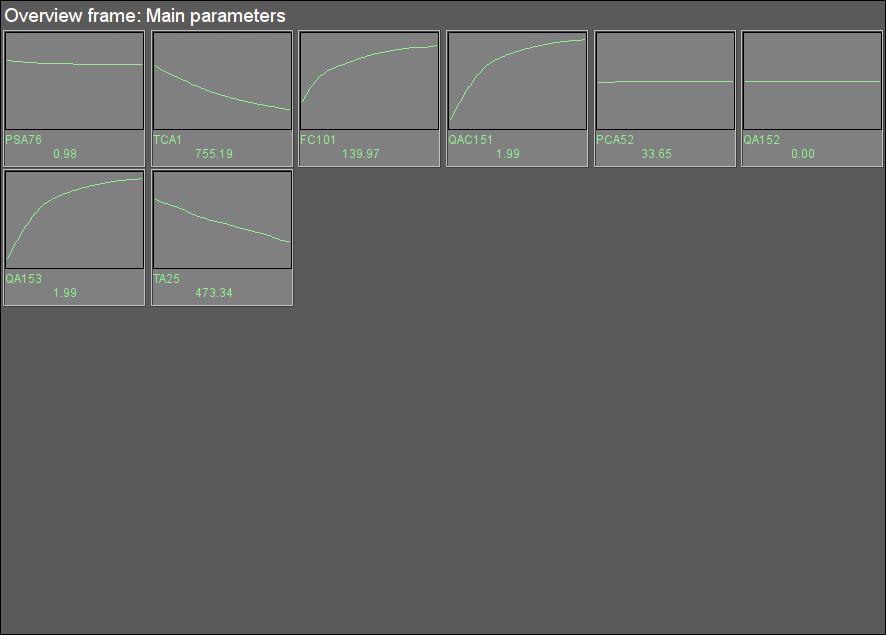
Fig. 46. Signal object "Economizer" overview group.
3.11 Signal object "AirSup"
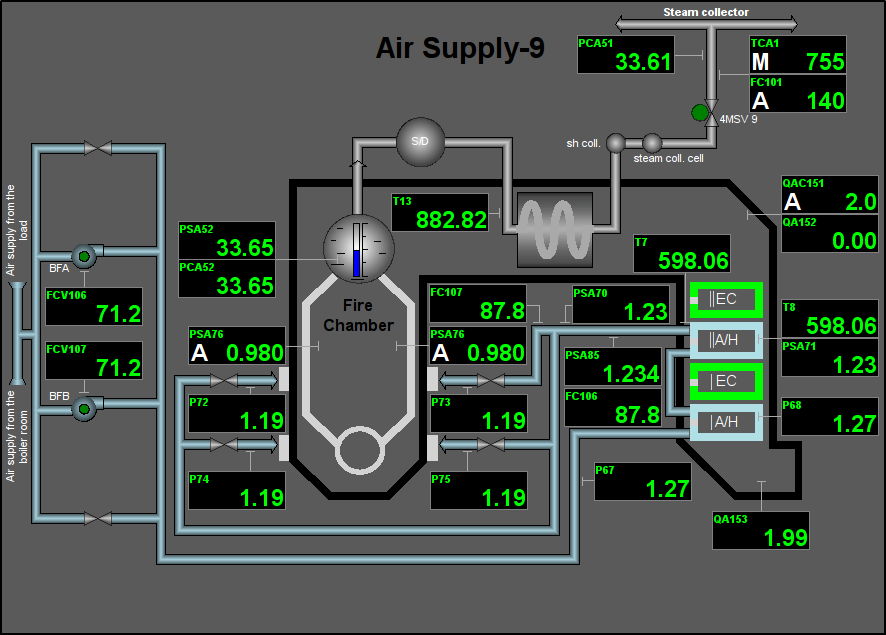
Fig. 47. Signal object "AirSup" mnemo.
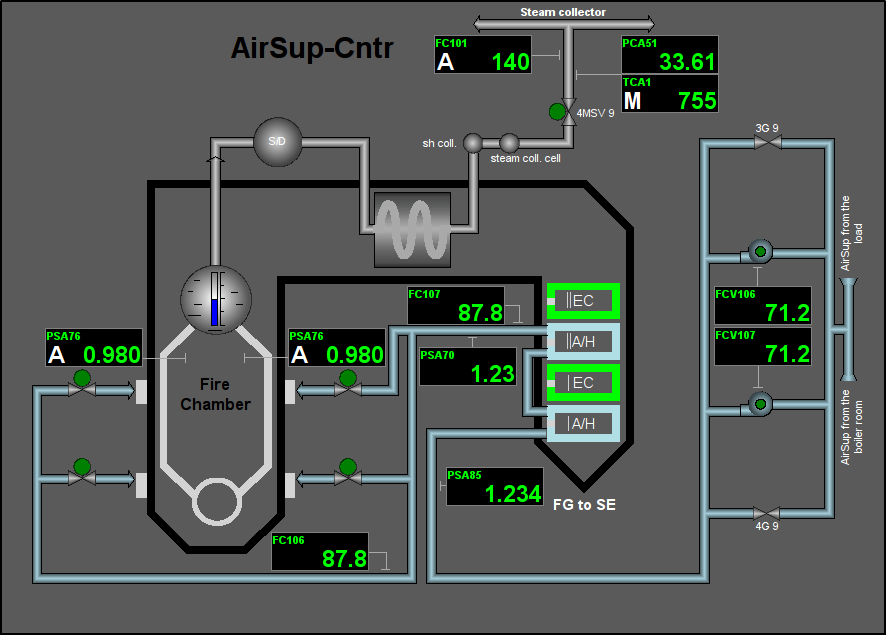
Fig. 48. Signal object "AirSup" mnemo 2.
Fig. 49. Signal object "AirSup" graphics group.
Fig. 50. Signal object "AirSup" contour group.
Fig. 51. Signal object "AirSup" overview group.
4 Results
The development result is complete dynamic model of the technological process of the multifuel steam boiler for the high pressure and high productivity. This model is available in three languages and is included to the OpenSCADA distributives to demonstrate the functions and features.
The model provides the availability to control of TP on behalf of the operator including the following operations:
- regulators control:
- regulator's mode change: "Automate", "Manual" and "Cascade";
- set of the desirable setpoint value or manual output of the executive mechanism;
- PID-regulator's parameters configuration.
In general, the following regulators take a full part at the control scheme :
- LC121 — level in the boiler's drum;
- PSA76 — the vacuum in the boiler furnace;
- FC101 — steam flow from the boiler;
- FC102 — natural gas flow;
- FC103, FC104 — flow of blast furnace gas on the left gas pipeline ;
- FC105 — flow of the coke oven gas;
- QAC151 — the percentage of oxygen in the flue gases;
- TCA1 — steam temperature at the outlet.
In an applied sense the model let us to work out the control algorithms of the multi fuel supply.
Resource consumption of the model is 70% for the CPU 800 MHz, x86 architecture.
Links